Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Variation within and across primary tumor sites, and implications for antigen-specific immunotherapy
- PMID: 33660372
- PMCID: PMC10320663
- DOI: 10.1002/hed.26662
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Variation within and across primary tumor sites, and implications for antigen-specific immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study is to describe human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2) overexpression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and re-evaluate its potential as a target for HER2-directed immunotherapies.
Methods: A retrospective cohort of patients with HNSCC receiving curative treatment was identified, and HER2 expression evaluated in archival tissue by immunohistochemistry and correlated with clinicopathological characteristics. HER2 expression data were also determined for HNSCC patients in The Cancer Genome Atlas.
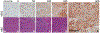
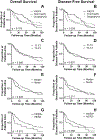
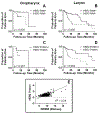
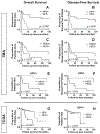
Results: Nineteen percent of HNSCC and 39% of oropharyngeal HNSCC (OPSCC) were HER2 positive. HER2 expression positively correlated with nodal metastasis (p = 0.035). Patients with HER2-positive tumors had decreased overall survival (p = 0.012), including within the human papilloma virus-positive OPSCC subgroup (p = 0.007).
Conclusions: A substantial fraction of HNSCC overexpresses HER2 protein, suggesting it may be a suitable target for antigen-directed immunotherapy. HER2 expression and its correlation with survival vary across HNSCC subsites, making it unsuitable as a prognostic marker.
Keywords: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 human papilloma virus immunotherapy oropharynx.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Contents do not represent the views of the US Department of Veterans Affairs or the US Government. The authors report no conflicts of interest for the existing work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heregulin and HER3 are prognostic biomarkers in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer. 2015 Oct 15;121(20):3600-11. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29549. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26195293 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic alterations in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2/ERBB2) in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Head Neck. 2017 Jan;39(1):E15-E19. doi: 10.1002/hed.24587. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Head Neck. 2017. PMID: 27653501
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 neu expression in head and neck squamous cell cancers and its clinicopathological correlation: Results from an Indian cancer center.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2018 Jul-Sep;61(3):313-318. doi: 10.4103/0377-4929.236599. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30004046
-
Brain metastasis from squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a review of the literature in the genomic era.Neurosurg Focus. 2018 Jun;44(6):E11. doi: 10.3171/2018.2.FOCUS17761. Neurosurg Focus. 2018. PMID: 29852772 Review.
-
[Immunotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Feb 7;52(2):143-147. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2017.02.019. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28219181 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The Role of Tumor-Associated Antigen HER2/neu in Tumor Development and the Different Approaches for Using It in Treatment: Many Choices and Future Directions.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;14(24):6173. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246173. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy and potential mechanisms of pyrotinib in targeting EGFR and HER2 in advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Aug 6;24(1):898. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04459-4. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39107736 Free PMC article.
-
Shooting at Moving and Hidden Targets-Tumour Cell Plasticity and the Notch Signalling Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 10;13(24):6219. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246219. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Icarian flight of antibody-drug conjugates: target selection amidst complexity and tackling adverse impacts.Protein Cell. 2025 Jul 19;16(7):532-556. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwaf002. Protein Cell. 2025. PMID: 39813112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances and challenges in CAR-T cell therapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Biomark Res. 2025 May 1;13(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s40364-025-00783-1. Biomark Res. 2025. PMID: 40312353 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ang KK, Berkey BA, Tu X, et al. Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor expression on survival and pattern of relapse in patients with advanced head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res 2002;62(24):7350–7356. - PubMed
-
- Boyle JO, Hakim J, Koch W, et al. The incidence of P53 mutations increases with progression of head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 1993;53(19):4477–4480. - PubMed
-
- Grandis JR, Tweardy DJ. Elevated levels of transforming growth factor α and epidermal growth factor receptor messenger RNA are early markers of carcinogenesis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 1993;53(15):3579–3584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

