Therapeutic potential of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth infusion into patients with type 2 diabetes depends on basal lipid levels and islet function
- PMID: 33660433
- PMCID: PMC8235136
- DOI: 10.1002/sctm.20-0303
Therapeutic potential of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth infusion into patients with type 2 diabetes depends on basal lipid levels and islet function
Abstract
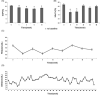
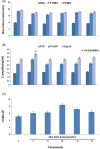
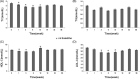
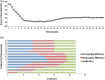
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) hold great potential in treating patients with diabetes, but the therapeutic effects are not always achieved. Particularly, the clinical factors regulating MSC therapy in this setting are largely unknown. In this study, 24 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) treated with insulin were selected to receive three intravenous infusions of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHED) over the course of 6 weeks and were followed up for 12 months. We observed a significant reduction of glycosylated serum albumin level (P < .05) and glycosylated hemoglobin level (P < .05) after SHED transplantation. The total effective rate was 86.36% and 68.18%, respectively, at the end of treatment and follow-up periods. Three patients ceased insulin injections after SHED transplantation. A steamed bread meal test showed that the serum levels of postprandial C-peptide at 2 hours were significantly higher than those at the baseline (P < .05). Further analysis showed that patients with a high level of blood cholesterol and a low baseline level of C-peptide had poor response to SHED transplantation. Some patients experienced a transient fever (11.11%), fatigue (4.17%), or rash (1.39%) after SHED transplantation, which were easily resolved. In summary, SHED infusion is a safe and effective therapy to improve glucose metabolism and islet function in patients with T2DM. Blood lipid levels and baseline islet function may serve as key factors contributing to the therapeutic outcome of MSC transplantation in patients with T2DM.
Keywords: diabetes; glucose metabolism; islet function; mesenchymal stem cells; stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth.
© 2021 The Authors. STEM CELLS TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;138:271‐281. - PubMed
-
- Ingelfinger JR, Jarcho JA, Ingelfinger JR, et al. Increase in the incidence of diabetes and its implications. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1473‐1474. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Krznar P, Erban A, et al. Metabolomics identifies a biomarker revealing in vivo loss of functional β cell mass before diabetes onset. Diabetes. 2019;68:2272‐2286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

