Manifestations and Outcome of Cardiac Sarcoidosis and Idiopathic Giant Cell Myocarditis by 25-Year Nationwide Cohorts
- PMID: 33660520
- PMCID: PMC8174201
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019415
Manifestations and Outcome of Cardiac Sarcoidosis and Idiopathic Giant Cell Myocarditis by 25-Year Nationwide Cohorts
Abstract
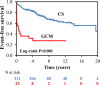
Background Cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) and giant cell myocarditis (GCM) share many histopathologic and clinical features. Whether they are parts of a one-disease continuum has been discussed. Methods and Results We compared medical record data of 351 CS and 28 GCM cases diagnosed in Finland since the late 1980s and followed until February 2018 for a composite end point of cardiac death, aborted sudden death, and heart transplantation. Heart failure was the presenting manifestation in 50% versus 15% (P<0.001), and high-grade atrioventricular block in 21% versus 43% (P=0.044), of GCM and CS, respectively. At presentation, left ventricular ejection fraction was ≤50% in 81% of cases of GCM versus in 48% of CS (P=0.004). The median (interquartile range) of plasma NT-proBNP (N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide) was 5273 (2782-11309) ng/L on admission in GCM versus 859 (290-1950) ng/L in CS (P<0.001), and cardiac troponin T exceeded 50 ng/L in 17 of 19 cases of GCM versus in 48 of 239 cases of CS (P<0.001). The 5-year estimate of event-free survival was 77% (95% CI, 72%-82%) in CS versus 27% (95% CI, 10%-45%) in GCM (P<0.001). By Cox regression analysis, GCM predicted cardiac events with a hazard ratio of 5.16 (95% CI, 2.82-9.45), which, however, decreased to 1.58 (95% CI, 0.71-3.52) after inclusion of markers of myocardial injury and dysfunction in the model. Conclusions GCM differs from CS in presenting with more extensive myocardial injury and having worse long-term outcome. Yet the key determinant of prognosis appears to be the extent of myocardial injury rather than the histopathologic diagnosis.
Keywords: cardiac sarcoidosis; giant cell myocarditis; inflammatory heart disease.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cardiac Sarcoidosis and Giant Cell Myocarditis: Actually, 2 Ends of the Same Disease?J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Mar 16;10(6):e020542. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.020542. Epub 2021 Mar 4. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33660527 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cardiac sarcoidosis and giant cell myocarditis as causes of atrioventricular block in young and middle-aged adults.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2011 Jun;4(3):303-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.110.959254. Epub 2011 Mar 22. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2011. PMID: 21427276
-
Idiopathic giant cell myocarditis or cardiac sarcoidosis? A retrospective audit of a nationwide case series.ESC Heart Fail. 2020 Jun;7(3):1362-1370. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12725. Epub 2020 Apr 28. ESC Heart Fail. 2020. PMID: 32343481 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis, management, and outcome of cardiac sarcoidosis and giant cell myocarditis: a Swedish single center experience.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Apr 26;22(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02639-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 35473644 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic giant cell myocarditis and cardiac sarcoidosis.Heart Fail Rev. 2013 Nov;18(6):733-46. doi: 10.1007/s10741-012-9358-3. Heart Fail Rev. 2013. PMID: 23111533 Review.
-
Short- and long-term outcomes after heart transplantation in cardiac sarcoidosis and giant-cell myocarditis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Res Cardiol. 2022 Feb;111(2):125-140. doi: 10.1007/s00392-021-01920-0. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Clin Res Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 34402927 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Clinical and Histological Intersection of Cardiac Sarcoidosis and Giant Cell Myocarditis.Cureus. 2024 May 7;16(5):e59783. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59783. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38846240 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and prognosis in acute myocarditis and unexplained acute chest pain: a nationwide longitudinal cohort study.Open Heart. 2025 Apr 4;12(1):e003050. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2024-003050. Open Heart. 2025. PMID: 40185500 Free PMC article.
-
A fearsome evolution of presumed cardiac sarcoidosis: The sarcoid-lymphoma syndrome.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024 Aug 26;54:101496. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101496. eCollection 2024 Oct. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024. PMID: 39280693 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Can FDG-PET Imaging Identify Cardiac Sarcoidosis Disease Phenotypes?Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024 Sep;26(9):851-857. doi: 10.1007/s11886-024-02086-7. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38990493 Review.
-
Cardiac Sarcoidosis and Giant Cell Myocarditis: Actually, 2 Ends of the Same Disease?J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Mar 16;10(6):e020542. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.020542. Epub 2021 Mar 4. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33660527 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Litovsky SH, Burke AP, Virmani R. Giant cell myocarditis: an entity distinct from sarcoidosis characterized by multiphasic myocyte destruction by cytotoxic T cells and histiocytic giant cells. Mod Pathol. 1996;9:1126–1134. - PubMed
-
- Cooper LT Jr, Berry GJ, Shabetai R. Idiopathic giant‐cell myocarditis—natural history and treatment. Multicenter Giant Cell Myocarditis Study Group Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1860–1866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

