Optimization of dose and route of administration of the P-glycoprotein inhibitor, valspodar (PSC-833) and the P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein dual-inhibitor, elacridar (GF120918) as dual infusion in rats
- PMID: 33660938
- PMCID: PMC7931226
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.740
Optimization of dose and route of administration of the P-glycoprotein inhibitor, valspodar (PSC-833) and the P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein dual-inhibitor, elacridar (GF120918) as dual infusion in rats
Abstract
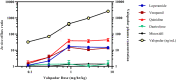
Transporters can play a key role in the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs. Understanding these contributions early in drug discovery allows for more accurate projection of the clinical pharmacokinetics. One method to assess the impact of transporters in vivo involves co-dosing specific inhibitors. The objective of the present study was to optimize the dose and route of administration of a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitor, valspodar (PSC833), and a dual P-gp/breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) inhibitor, elacridar (GF120918), by assessing the transporters' impact on brain penetration and absorption. A dual-infusion strategy was implemented to allow for flexibility with dose formulation. The chemical inhibitor was dosed intravenously via the femoral artery, and a cassette of known substrates was infused via the jugular vein. Valspodar or elacridar was administered as 4.5-hour constant infusions over a range of doses. To assess the degree of inhibition, the resulting ratios of brain and plasma concentrations, Kp's, of the known substrates were compared to the vehicle control. These data demonstrated that doses greater than 0.9 mg/hr/kg valspodar and 8.9 mg/hr/kg elacridar were sufficient to inhibit P-gp- and BCRP-mediated efflux at the blood-brain barrier in rats without any tolerability issues. Confirmation of BBB restriction by efflux transporters in preclinical species allows for subsequent prediction in humans based upon the proteomic expression at rodent and human BBB. Overall, the approach can also be applied to inhibition of efflux at other tissues (gut absorption, liver clearance) or can be extended to other transporters of interest using alternate inhibitors.
Keywords: BCRP; Breast cancer resistance protein; IVIVC; Kp; P-glycoprotein; P-gp; blood-brain barrier; chemical and genetic knock out; dantrolene; efflux transporter; elacridar; glyburide; loperamide; quinidine; rat; valspodar; verapamil.
© 2021 The Authors. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd, British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. All co‐authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript and there is no financial interest to report. We certify that the submission is original work and is not under review at any other publication.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Saturable active efflux by p-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein at the blood-brain barrier leads to nonlinear distribution of elacridar to the central nervous system.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Apr;345(1):111-24. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.199786. Epub 2013 Feb 8. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013. PMID: 23397054 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous infusion for the controlled exposure to the dual ABCB1 and ABCG2 inhibitor elacridar in nonhuman primates.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018 Jun;8(3):536-542. doi: 10.1007/s13346-017-0472-6. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29294257
-
Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption Increases Amyloid-Related Pathology in TgSwDI Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 27;22(3):1231. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031231. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33513818 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the in vitro and in vivo methods to assess impact of P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein transporters in central nervous system drug disposition.Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2023 Feb;44(1):7-25. doi: 10.1002/bdd.2345. Epub 2023 Feb 5. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2023. PMID: 36692150 Review.
-
Radioligands targeting P-glycoprotein and other drug efflux proteins at the blood-brain barrier.J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2013 Mar-Apr;56(3-4):68-77. doi: 10.1002/jlcr.2993. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2013. PMID: 24285312 Review.
Cited by
-
Applicability of MDR1 Overexpressing Abcb1KO-MDCKII Cell Lines for Investigating In Vitro Species Differences and Brain Penetration Prediction.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 29;16(6):736. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060736. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931858 Free PMC article.
-
Elacridar Inhibits BCRP Protein Activity in 2D and 3D Cell Culture Models of Ovarian Cancer and Re-Sensitizes Cells to Cytotoxic Drugs.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 17;26(12):5800. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125800. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565261 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Substituted Di(pyridin-2-yl)-1,2,4-thiadiazol-5-amines as Novel Macrofilaricidal Compounds for the Treatment of Human Filarial Infections.J Med Chem. 2022 Aug 25;65(16):11388-11403. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00960. Epub 2022 Aug 16. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35972896 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Functional Evaluation of a Three-Dimensional Blood-Brain Barrier Model Equipped With Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells.Pharm Res. 2022 Jul;39(7):1535-1547. doi: 10.1007/s11095-022-03249-3. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 35411503 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug Resistance of Cancer Cells and the Vital Role of P-Glycoprotein.Life (Basel). 2022 Jun 15;12(6):897. doi: 10.3390/life12060897. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35743927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uchida Y, Ohtsuki S, Kamiie J, Terasaki T. Blood‐brain barrier (BBB) pharmacoproteomics: reconstruction of in vivo brain distribution of 11 P‐glycoprotein substrates based on the BBB transporter protein concentration, in vitro intrinsic transport activity, and unbound fraction in plasma and brain in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;339(2):579‐588. - PubMed
-
- Chu X, Zhang Z, Yabut J, et al. Characterization of multidrug resistance 1a/P‐glycoprotein knockout rats generated by zinc finger nucleases. Mol Pharmacol. 2012;81(2):220‐227. - PubMed
-
- Dufek MB, Knight BM, Bridges AS, Thakker DR. P‐glycoprotein increases portal bioavailability of loperamide in mouse by reducing first‐pass intestinal metabolism. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013;41(3):642‐650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

