Pulmonary, cardiac and renal distribution of ACE2, furin, TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 in rats with heart failure: Potential implication for COVID-19 disease
- PMID: 33660945
- PMCID: PMC8014258
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16310
Pulmonary, cardiac and renal distribution of ACE2, furin, TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 in rats with heart failure: Potential implication for COVID-19 disease
Abstract
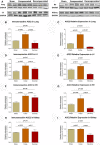
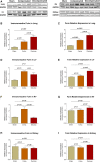
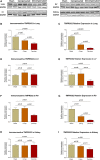
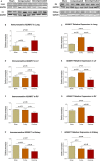
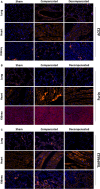
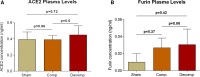
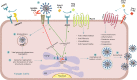
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is often associated with kidney and pulmonary dysfunction. Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) contributes to avid sodium retention, cardiac hypertrophy and oedema formation, including lung congestion. While the status of the classic components of RAAS such as renin, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin II (Ang II) and angiotensin II receptor AT-1 is well studied in CHF, the expression of angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE2), a key enzyme of angiotensin 1-7 (Ang 1-7) generation in the pulmonary, cardiac and renal systems has not been studied thoroughly in this clinical setting. This issue is of a special interest as Ang 1-7 counterbalance the vasoconstrictory, pro-inflammatory and pro-proliferative actions of Ang II. Furthermore, CHF predisposes to COVID-19 disease severity, while ACE2 also serves as the binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 in human host-cells, and acts in concert with furin, an important enzyme in the synthesis of BNP in CHF, in permeating viral functionality along TMPRSST2. ADAM17 governs ACE2 shedding from cell membranes. Therefore, the present study was designed to investigate the expression of ACE2, furin, TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 in the lung, heart and kidneys of rats with CHF to understand the exaggerated susceptibility of clinical CHF to COVID-19 disease. Heart failure was induced in male Sprague Dawley rats by the creation of a surgical aorto-caval fistula. Sham-operated rats served as controls. One week after surgery, the animals were subdivided into compensated and decompensated CHF according to urinary sodium excretion. Both groups and their controls were sacrificed, and their hearts, lungs and kidneys were harvested for assessment of tissue remodelling and ACE2, furin, TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 immunoreactivity, expression and immunohistochemical staining. ACE2 immunoreactivity and mRNA levels increased in pulmonary, cardiac and renal tissues of compensated, but not in decompensated CHF. Furin immunoreactivity was increased in both compensated and decompensated CHF in the pulmonary, cardiac tissues and renal cortex but not in the medulla. Interestingly, both the expression and abundance of pulmonary, cardiac and renal TMPRSS2 decreased in CHF in correlation with the severity of the disease. Pulmonary, cardiac and renal ADAM17 mRNA levels were also downregulated in decompensated CHF. Circulating furin levels increased in proportion to CHF severity, whereas plasma ACE2 remained unchanged. In summary, ACE2 and furin are overexpressed in the pulmonary, cardiac and renal tissues of compensated and to a lesser extent of decompensated CHF as compared with their sham controls. The increased expression of the ACE2 in heart failure may serve as a compensatory mechanism, counterbalancing the over-activity of the deleterious isoform, ACE. Downregulated ADAM17 might enhance membranal ACE2 in COVID-19 disease, whereas the suppression of TMPRSS2 in CHF argues against its involvement in the exaggerated susceptibility of CHF patients to SARS-CoV2.
Keywords: ADAM17; TMPRSS2; angiotensin converting enzyme 2; furin; heart; heart failure; kidney; lung.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflicting interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cardiac and renal distribution of ACE and ACE-2 in rats with heart failure.Acta Histochem. 2014 Oct;116(8):1342-9. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Sep 10. Acta Histochem. 2014. PMID: 25217176
-
A pressor dose of angiotensin II has no influence on the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and other molecules associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice.FASEB J. 2021 Mar;35(3):e21419. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100016R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33566370 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of renin-angiotensin system and COVID-19: the importance of daily rhythms in ACE2, ADAM17 and TMPRSS2 expression.Physiol Res. 2021 Dec 16;70(S2):S177-S194. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934754. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 34913351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesogenic and Ketogenic Diets Distinctly Regulate the SARS-CoV-2 Entry Proteins ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and the Renin-Angiotensin System in Rat Lung and Heart Tissues.Nutrients. 2021 Sep 25;13(10):3357. doi: 10.3390/nu13103357. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34684358 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of SARS-CoV-2 on Cardiovascular System: The Dual Role of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) as the Virus Receptor and Homeostasis Regulator-Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 26;22(9):4526. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094526. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33926110 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting susceptibility to COVID-19 infection in patients on maintenance hemodialysis by cross-coupling soluble ACE2 concentration with lymphocyte count: an algorithmic approach.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 30;11:1444719. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1444719. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39540040 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Furin and Its Therapeutic Potential in Cardiovascular Disease Risk.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 26;25(17):9237. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179237. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 and protection against reinfection in rats.Zool Res. 2022 Nov 18;43(6):945-948. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.339. Zool Res. 2022. PMID: 36208120 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The endocrine basis of the cardio-renal axis: New perspectives regarding corin.Physiol Rep. 2024 Jul;12(13):e16105. doi: 10.14814/phy2.16105. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38942727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pioglitazone Synthetic Analogue Ameliorates Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mellitus through Modulation of ACE 2/Angiotensin 1-7 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Mar 10;15(3):341. doi: 10.3390/ph15030341. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35337139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Epidemiology Working Group for Ncip Epidemic Response CCfDC, Prevention . The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID‐19) in China. Zhonghua liu xing bing xue za zhi. 2020;41(2):145‐151. - PubMed
-
- Bonow RO, Fonarow GC, O'Gara PT, Yancy CW. Association of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) with myocardial injury and mortality. JAMA Cardiol. 2020.5(7):751–753. - PubMed
-
- Liu PP, Blet A, Smyth D, Li H. The science underlying COVID‐19: implications for the cardiovascular system. Circulation. 2020;142(1):68‐78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

