Genomic characterization and evolution of SARS-CoV-2 of a Canadian population
- PMID: 33662015
- PMCID: PMC7932534
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247799
Genomic characterization and evolution of SARS-CoV-2 of a Canadian population
Abstract
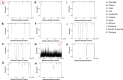
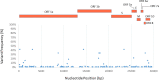
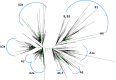
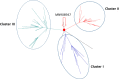
COVID-19 has greatly affected public health and world economy. In this study, we analyzed 129 full-length genomes of SARS-CoV-2 viruses of a Canadian population during early phase of the pandemic. Phylogenetic analysis revealed three major paths of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 viruses into Canada. Twenty-one substitutions that have frequencies greater than 3% of viral population were identified. Analysis of these substitutions indicated that P1427I (ORF1b), Y1464C (ORF1b), and Q57H (ORF3a) might affect functions of the corresponding SARS-CoV-2 encoded proteins. Additionally, we found the evidence of positive selection on the ORF3a and codon 614 of Spike protein, suggesting the viral components responsible for host entry and activation of inflammation response were targeted by host immune responses. The study showed genomic variation and evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in a Canadian population. These information may help develop preventive strategies and be used for further study of SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis and therapeutics development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The extent of molecular variation in novel SARS-CoV-2 after the six-month global spread.Infect Genet Evol. 2021 Jul;91:104800. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104800. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Infect Genet Evol. 2021. PMID: 33677109 Free PMC article.
-
Global variation in SARS-CoV-2 proteome and its implication in pre-lockdown emergence and dissemination of 5 dominant SARS-CoV-2 clades.Infect Genet Evol. 2021 Sep;93:104973. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104973. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Infect Genet Evol. 2021. PMID: 34147651 Free PMC article.
-
A Gapless, Unambiguous RNA Metagenome-Assembled Genome Sequence of a Unique SARS-CoV-2 Variant Encoding Spike S813I and ORF1a A859V Substitutions.OMICS. 2021 Feb;25(2):123-128. doi: 10.1089/omi.2020.0194. Epub 2020 Nov 30. OMICS. 2021. PMID: 33253058
-
SARS-CoV-2 Entry Related Viral and Host Genetic Variations: Implications on COVID-19 Severity, Immune Escape, and Infectivity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 17;22(6):3060. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063060. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Infection: New Molecular, Phylogenetic, and Pathogenetic Insights. Efficacy of Current Vaccines and the Potential Risk of Variants.Viruses. 2021 Aug 25;13(9):1687. doi: 10.3390/v13091687. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34578269 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Functional Consequences of the Novel Ribosomal Pausing Site in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein RNA.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 17;22(12):6490. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126490. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34204305 Free PMC article.
-
The Algerian Chapter of SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: An Evolutionary, Genetic, and Epidemiological Prospect.Viruses. 2021 Aug 2;13(8):1525. doi: 10.3390/v13081525. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452390 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Role of SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a in Viral Pathogenesis and COVID-19.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 9;13:854567. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.854567. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35356515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-resolution analysis of long-term serum antibodies in humans following convalescence of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Sci Rep. 2022 May 31;12(1):9045. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12032-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35641545 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Genome Variations in Viral Shedding of an Immunocompromised Patient with Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma.Viruses. 2023 Jan 28;15(2):377. doi: 10.3390/v15020377. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851588 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

