The prognostic value of serum albumin levels and respiratory rate for community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective, multi-center study
- PMID: 33662036
- PMCID: PMC7932099
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248002
The prognostic value of serum albumin levels and respiratory rate for community-acquired pneumonia: A prospective, multi-center study
Abstract
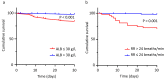
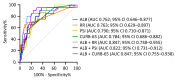
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a respiratory disease frequently requiring hospital admission, and a significant cause of death worldwide. This study aimed to investigate the prognostic value of clinical indicators. A prospective, multi-center study was conducted (January 2017-December 2018) where patient demographic and clinical data were recorded (N = 366). The 30-day mortality rate was 5.46%. Cox Regression analyses showed that serum albumin (ALB) and respiratory rate (RR) were independent prognostic variables for 30-day survival in patients with CAP. Albumin negatively correlated with the Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI) and CURB-65 scores using Pearson and Spearman tests. Survival curves showed that a RR >24 breaths/min or ALB ≤30 g/L were associated with a significantly higher risk of mortality. The area-under-the-curve (AUC) for predicting 30-day mortality in patients with CAP was 0.762, 0.763, 0.790, and 0.784 for ALB, RR, PSI, and CURB-65, respectively. The AUC for the prediction of 30-day mortality using ALB combined with PSI, CURB-65 scores, and RR was 0.822 (95% CI 0.731-0.912), 0.847 (95% CI 0.755-0.938), and 0.847 (95% CI 0.738-0.955), respectively. Albumin and RR were found to be reliable prognostic factors for CAP. This combination showed equal predictive value when compared to adding ALB assessment to PSI and CURB-65 scores, which could improve their prognostic accuracy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Song JH, Oh WS, Kang CI, Chung DR, Peck KR, Ko KS, et al.. Epidemiology and clinical outcomes of community-acquired pneumonia in adult patients in Asian countries: a prospective study by the Asian network for surveillance of resistant pathogens. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2008;31:107–14. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.09.014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

