Effect of Ivermectin on Time to Resolution of Symptoms Among Adults With Mild COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 33662102
- PMCID: PMC7934083
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2021.3071
Effect of Ivermectin on Time to Resolution of Symptoms Among Adults With Mild COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Ivermectin is widely prescribed as a potential treatment for COVID-19 despite uncertainty about its clinical benefit.
Objective: To determine whether ivermectin is an efficacious treatment for mild COVID-19.
Design, setting, and participants: Double-blind, randomized trial conducted at a single site in Cali, Colombia. Potential study participants were identified by simple random sampling from the state's health department electronic database of patients with symptomatic, laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 during the study period. A total of 476 adult patients with mild disease and symptoms for 7 days or fewer (at home or hospitalized) were enrolled between July 15 and November 30, 2020, and followed up through December 21, 2020.
Intervention: Patients were randomized to receive ivermectin, 300 μg/kg of body weight per day for 5 days (n = 200) or placebo (n = 200).
Main outcomes and measures: Primary outcome was time to resolution of symptoms within a 21-day follow-up period. Solicited adverse events and serious adverse events were also collected.
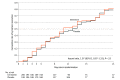
Results: Among 400 patients who were randomized in the primary analysis population (median age, 37 years [interquartile range {IQR}, 29-48]; 231 women [58%]), 398 (99.5%) completed the trial. The median time to resolution of symptoms was 10 days (IQR, 9-13) in the ivermectin group compared with 12 days (IQR, 9-13) in the placebo group (hazard ratio for resolution of symptoms, 1.07 [95% CI, 0.87 to 1.32]; P = .53 by log-rank test). By day 21, 82% in the ivermectin group and 79% in the placebo group had resolved symptoms. The most common solicited adverse event was headache, reported by 104 patients (52%) given ivermectin and 111 (56%) who received placebo. The most common serious adverse event was multiorgan failure, occurring in 4 patients (2 in each group).
Conclusion and relevance: Among adults with mild COVID-19, a 5-day course of ivermectin, compared with placebo, did not significantly improve the time to resolution of symptoms. The findings do not support the use of ivermectin for treatment of mild COVID-19, although larger trials may be needed to understand the effects of ivermectin on other clinically relevant outcomes.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04405843.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

