Clonazepam-induced lichenoid drug eruption: a case report
- PMID: 33663441
- PMCID: PMC7934486
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-021-03132-2
Clonazepam-induced lichenoid drug eruption: a case report
Abstract
Background: Lichenoid drug eruption is rare and can mimic idiopathic lichen planus and other dermatoses. Clonazepam, a commonly used drug for the treatment of anxiety-related disorders and seizures, is known to be an unlikely cause of cutaneous adverse effects. Only one case report of LDE due to clonazepam has been reported.
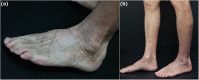
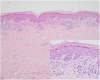
Case presentation: A 81-year-old male patient with Alzheimer's disease developed a lichenoid eruption after taking clonazepam. He developed a violaceous scaly patch on his lower extremities, from both buttocks to the feet. The cutaneous eruption resolved 2 months after cessation of clonazepam and with initiation of corticosteroid therapy.
Conclusion: A skin eruption that develops after clonazepam administration can be a lichenoid drug eruption, which is less likely to resolve spontaneously and requires discontinuation of clonazepam administration.
Keywords: Clonazepam; Cutaneous; Drug eruption; Lichenoid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- US FDA . Klonopin tablets (clonazepam) Klonopin wafers (clonazepam orally disintegrating tablets) 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources