Ambient noise exposure induces long-term adaptations in adult brainstem neurons
- PMID: 33664302
- PMCID: PMC7933235
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-84230-9
Ambient noise exposure induces long-term adaptations in adult brainstem neurons
Abstract
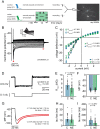
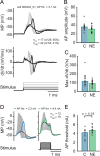
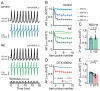
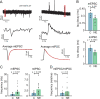
To counterbalance long-term environmental changes, neuronal circuits adapt the processing of sensory information. In the auditory system, ongoing background noise drives long-lasting adaptive mechanism in binaural coincidence detector neurons in the superior olive. However, the compensatory cellular mechanisms of the binaural neurons in the medial superior olive (MSO) to long-term background changes are unexplored. Here we investigated the cellular properties of MSO neurons during long-lasting adaptations induced by moderate omnidirectional noise exposure. After noise exposure, the input resistance of MSO neurons of mature Mongolian gerbils was reduced, likely due to an upregulation of hyperpolarisation-activated cation and low voltage-activated potassium currents. Functionally, the long-lasting adaptations increased the action potential current threshold and facilitated high frequency output generation. Noise exposure accelerated the occurrence of spontaneous postsynaptic currents. Together, our data suggest that cellular adaptations in coincidence detector neurons of the MSO to continuous noise exposure likely increase the sensitivity to differences in sound pressure levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adaptation of binaural processing in the adult brainstem induced by ambient noise.J Neurosci. 2012 Jan 11;32(2):462-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2094-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22238082 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-Dependent Calcium Signaling in Neurons of the Medial Superior Olive during Late Postnatal Development.J Neurosci. 2020 Feb 19;40(8):1689-1700. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1545-19.2020. Epub 2020 Jan 16. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31949105 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting binaural responses from monaural responses in the gerbil medial superior olive.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Jun 1;115(6):2950-63. doi: 10.1152/jn.01146.2015. Epub 2016 Mar 23. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 27009164 Free PMC article.
-
The ion channels and synapses responsible for the physiological diversity of mammalian lower brainstem auditory neurons.Hear Res. 2019 May;376:33-46. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2018.12.011. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Hear Res. 2019. PMID: 30606624 Review.
-
Roles of inhibition for transforming binaural properties in the brainstem auditory system.Hear Res. 2002 Jun;168(1-2):60-78. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5955(02)00362-3. Hear Res. 2002. PMID: 12117510 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular and synaptic specializations for sub-millisecond precision in the mammalian auditory brainstem.Front Cell Neurosci. 2025 May 19;19:1568506. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1568506. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40458470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to discern external acoustic waves in a piezoelectric neuron under noise?J Biol Phys. 2022 Sep;48(3):339-353. doi: 10.1007/s10867-022-09611-1. Epub 2022 Aug 10. J Biol Phys. 2022. PMID: 35948818 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

