Potential neutralizing antibodies discovered for novel corona virus using machine learning
- PMID: 33664393
- PMCID: PMC7970853
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-84637-4
Potential neutralizing antibodies discovered for novel corona virus using machine learning
Abstract
The fast and untraceable virus mutations take lives of thousands of people before the immune system can produce the inhibitory antibody. The recent outbreak of COVID-19 infected and killed thousands of people in the world. Rapid methods in finding peptides or antibody sequences that can inhibit the viral epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 will save the life of thousands. To predict neutralizing antibodies for SARS-CoV-2 in a high-throughput manner, in this paper, we use different machine learning (ML) model to predict the possible inhibitory synthetic antibodies for SARS-CoV-2. We collected 1933 virus-antibody sequences and their clinical patient neutralization response and trained an ML model to predict the antibody response. Using graph featurization with variety of ML methods, like XGBoost, Random Forest, Multilayered Perceptron, Support Vector Machine and Logistic Regression, we screened thousands of hypothetical antibody sequences and found nine stable antibodies that potentially inhibit SARS-CoV-2. We combined bioinformatics, structural biology, and Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations to verify the stability of the candidate antibodies that can inhibit SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
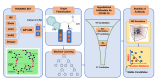
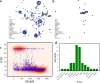
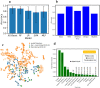
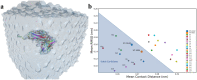
Similar articles
-
Peptide microarrays coupled to machine learning reveal individual epitopes from human antibody responses with neutralizing capabilities against SARS-CoV-2.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022 Dec;11(1):1037-1048. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2057874. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022. PMID: 35320064 Free PMC article.
-
Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants.Elife. 2020 Oct 28;9:e61312. doi: 10.7554/eLife.61312. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33112236 Free PMC article.
-
Potent neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern by an antibody with an uncommon genetic signature and structural mode of spike recognition.Cell Rep. 2021 Oct 5;37(1):109784. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109784. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34592170 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of Neutralization Assays and International Standard for Detecting SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody.Viruses. 2022 Jul 18;14(7):1560. doi: 10.3390/v14071560. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35891540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain by neutralizing antibodies.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 29;538:192-203. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.012. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33069360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence for COVID-19 Drug Discovery and Vaccine Development.Front Artif Intell. 2020 Aug 18;3:65. doi: 10.3389/frai.2020.00065. eCollection 2020. Front Artif Intell. 2020. PMID: 33733182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of artificial intelligence in COVID-19 medical area: a systematic review.J Thorac Dis. 2021 Dec;13(12):7034-7053. doi: 10.21037/jtd-21-747. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 35070385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NABP-BERT: NANOBODY®-antigen binding prediction based on bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) architecture.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Nov 22;26(1):bbae518. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae518. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39688476 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence-driven assessment of radiological images for COVID-19.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Sep;136:104665. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104665. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34343890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of blood-brain barrier and Caco-2 permeability through the Enalos Cloud Platform: combining contrastive learning and atom-attention message passing neural networks.J Cheminform. 2025 May 5;17(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13321-025-01007-2. J Cheminform. 2025. PMID: 40325398 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Z, Yi Y, Luo X, Xiong N, Liu Y, Li S, Sun R, Wang Y, Hu B, Chen W, Zhang Y, Wang J, Huang B, Lin Y, Yang J, Cai W, Wang X, Cheng J, Chen Z, Sun K, Pan W, Zhan Z, Chen L, Ye F. Development and clinical application of a rapid IgM–IgG combined antibody test for SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis. J. Med. Virol. 2020 doi: 10.1002/jmv.25727. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, Chen Y-M, Wang W, Song Z-G, Hu Y, Tao Z-W, Tian J-H, Pei Y-Y, Yuan M-L, Zhang Y-L, Dai F-H, Liu Y, Wang Q-M, Zheng J-J, Xu L, Holmes EC, Zhang Y-Z. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature. 2020 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ardabili SF, Mosavi A, Ghamisi P, Ferdinand F, Varkonyi-Koczy AR, Reuter U, Rabczuk T, Atkinson PM. COVID-19 outbreak prediction with machine learning. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.04.17.20070094. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

