An association between body image dissatisfaction and digit ratio among Chinese children and adolescents
- PMID: 33664410
- PMCID: PMC7970844
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-84711-x
An association between body image dissatisfaction and digit ratio among Chinese children and adolescents
Abstract
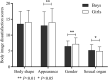
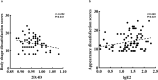
Body image dissatisfaction (BID) is a negative evaluation of personal physical characteristics, including dissatisfaction with body shape, gender, sexual organs, appearance and so forth, and it plays an important role in growth and development. The second-to-fourth digit ratio (2D:4D) is recognized as a putative indicator of intra-uterine testosterone to estrogen ratio exposure, and it has been observed that higher levels of fetal testosterone exposure are associated with a lower 2D:4D. The present paper contributes to a better understanding of the biological underpinnings of BID by analyzing BID and the digit ratio (2D:4D). We found that the 2D:4D was positively related to appearance dissatisfaction in boys with first spermatorrhea, which means that low prenatal androgen exposure may increase boys' dissatisfaction with their appearance. In girls with breast development being lower than Tanner stage II, their 2D:4D was negatively related to their body shape dissatisfaction, which means that high prenatal androgen exposure may increase girls' dissatisfaction with their body shape. These results suggest that the prenatal androgen exposure level might play an important role in the body image dissatisfaction of the offspring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Odea JA. Encyclopedia of Body Image and Human Appearance. Academic Press; 2012. pp. 141–147.
-
- He C, Wang J, Guo G, Chen G, Xiao S. Mediation effect of depression between body dissatisfaction and eating disorders symptom in a sample of adolescents. Chin. Ment. Health J. 2016;30:835–839. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6729.2016.11.007. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

