Risk Factors and Comorbidities in Young Indian Patients with Hypertension: REAL YOUNG (Hypertension) Study
- PMID: 33664586
- PMCID: PMC7924245
- DOI: 10.2147/IBPC.S272548
Risk Factors and Comorbidities in Young Indian Patients with Hypertension: REAL YOUNG (Hypertension) Study
Abstract
Purpose: To analyze the risk factors and comorbidities among the young Indian adults with hypertension.
Patients and methods: This was a retrospective, multicentric real-world study which included patients diagnosed with and receiving treatment for hypertension. Data were collected from the medical records of clinics/hospitals across 623 study sites in India. Patients of either sex and aged 18-45 years were included. Demographic details (age, sex, anthropometric measurement), medical and family history, sedentary lifestyle, smoking status and alcohol consumption data were extracted. Descriptive and comparative analysis (Mann-Whitney U and chi-squared test) was done.
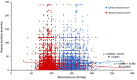
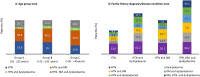
Results: Out of 15,006 young patients diagnosed with hypertension (men=63.6%), 65.7% belonged to the age group of >35-45 years. The median body mass index was 27.0 kg/m2. Patients diagnosed with only hypertension were 29.1% while other predominant comorbidities with hypertension were diabetes mellitus (42.4%) and dyslipidemia (7.8%). Hypertension with diabetes mellitus were prevalent in the age group of >35-45 years (43.8%). More than half of the patients with hypertension (n=7656) had a sedentary lifestyle. Overall, 35.6%, 47.3%, and 56.7% of the patients were alcoholic, smokers (present and former), and had a family history of hypertension, respectively.
Conclusion: The results showed that among the young population, hypertension was common in the age group of >35-45 years and diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia were common comorbidities. Family history, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, alcohol consumption, and body mass index may also contribute to hypertension.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; dyslipidemia; prevalence; young population.
© 2021 Desai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Mahesh Abhyankar and Dr Santosh Revankar are employees of USV Pvt. Ltd. Mahesh V Abhyankar reports personal fees from USV Pvt. Ltd, during the conduct of the study. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Undhad AM, Bharodiya PJ, Sonani RP. Correlates of hypertension among the bank employees of Surat city of Gujarat. Natl J Community Med. 2011;2(1):112–123.
-
- World Health Organization, World Health Statistics: a snapshot of global health; 2012. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/70889/WHO_IER_HSI_12.1_.... Accessed March02, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. Global action plan for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases 2013–2020. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2013. Available from: https://www.who.int/nmh/events/ncd_action_plan/en/Accessed. Accessed March02, 2020.
-
- Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(33):3021–3104. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources