Surface NKG2C Identifies Differentiated αβT-Cell Clones Expanded in Peripheral Blood
- PMID: 33664730
- PMCID: PMC7921799
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.613882
Surface NKG2C Identifies Differentiated αβT-Cell Clones Expanded in Peripheral Blood
Abstract
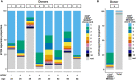
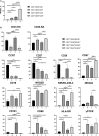
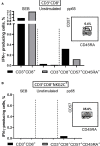
T cells that express CD56 in peripheral blood of healthy humans represent a heterogeneous and poorly studied subset. In this work, we analyzed this subset for NKG2C expression. In both CD56+ and CD56- subsets most of the NKG2C+ T cells had a phenotype of highly differentiated CD8+ TEMRA cells. The CD56+NKG2C+ T cells also expressed a number of NK cell receptors, such as NKG2D, CD16, KIR2DL2/DL3, and maturation marker CD57 more often than the CD56-NKG2C+CD3+ cells. TCR β-chain repertoire of the CD3+CD56+NKG2C+ cell fraction was limited by the prevalence of one or several clonotypes which can be found within the most abundant clonotypes in total or CD8+ T cell fraction TCRβ repertoire. Thus, NKG2C expression in highly differentiated CD56+ T cells was associated with the most expanded αβ T cell clones. NKG2C+ T cells produced almost no IFN-γ in response to stimulation with HCMV pp65-derived peptides. This may be partially due to the high content of CD45RA+CD57+ cells in the fraction. CD3+NKG2C+ cells showed signs of activation, and the frequency of this T-cell subset in HCMV-positive individuals was positively correlated with the frequency of NKG2C+ NK cells that may imply a coordinated in a certain extent development of the NKG2C+ T and NK cell subsets under HCMV infection.
Keywords: NKG2C; NKT-like cells; T cell differentiation; TCR repertoire; cytomegalovirus infection.
Copyright © 2021 Kovalenko, Zvyagin, Streltsova, Mikelov, Erokhina, Telford, Sapozhnikov and Lebedev.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Huard B, Karlsson L. A subpopulation of CD8+ T cells specific for melanocyte differentiation antigens expresses killer inhibitory receptors (KIR) in healthy donors: Evidence for a role of KIR in the control of peripheral tolerance. Eur J Immunol (2000) 30:1665–75. 10.1002/1521-4141(200006)30:6<1665::AID-IMMU1665>3.0.CO;2-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Speiser DE, Valmori D, Rimoldi D, Pittet MJ, Liénard D, Cerundolo V, et al. . CD28-negative cytolytic effector T cells frequently express NK receptors and are present at variable proportions in circulating lymphocytes from healthy donors and melanoma patients. Eur J Immunol (1999) 29:1990–9. 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199906)29:06<1990::AID-IMMU1990>3.0.CO;2-9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

