Therapeutic Effects of (5R)-5-Hydroxytriptolide on Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis via lncRNA WAKMAR2/miR-4478/E2F1/p53 Axis
- PMID: 33664742
- PMCID: PMC7921149
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.605616
Therapeutic Effects of (5R)-5-Hydroxytriptolide on Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis via lncRNA WAKMAR2/miR-4478/E2F1/p53 Axis
Abstract
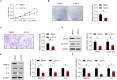
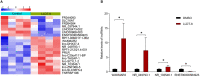
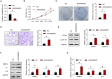
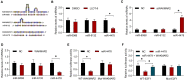
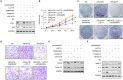
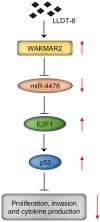
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) serve a major role in synovial hyperplasia and inflammation in RA. (5R)-5-hydroxytriptolide (LLDT-8), a novel triptolide derivative, shows promising therapeutic effects for RA and is now in phase II clinical trials in China. However, the underlying mechanism of LLDT-8 is still not fully understood. Here, we found that LLDT-8 inhibited proliferation and invasion of RA FLS, as well as the production of cytokines. Microarray data demonstrated that LLDT-8 upregulated the expression of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) WAKMAR2, which was negatively associated with proliferation and invasion of RA FLS, as well as the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Knockdown of WAKMAR2 abolished the inhibitory effects of LLDT-8 on RA FLS. Mechanistically, WAKMAR2 sponged miR-4478, which targeted E2F1 and downstreamed p53 signaling. Rescue experiments indicated that the inhibitory effects of LLDT-8 on RA FLS were dependent on WAKMAR2/miR-4478/E2F1/p53 axis.
Keywords: (5R)-5-hydroxytriptolide; WAKMAR2; fibroblast-like synoviocytes; inflammation; miR-4478/E2F1/p53 axis; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, Xie, Huang, Lu, Wang, Jin, Zhang, Chang, Xu, Xu, Fan, Liang and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
(5R)-5-Hydroxytriptolide (LLDT-8) induces substantial epigenetic mediated immune response network changes in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 1;9(1):11155. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47411-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31371761 Free PMC article.
-
Triptolide decreases rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte proliferation, invasion, inflammation and presents a therapeutic effect in collagen-induced arthritis rats via inactivating lncRNA RP11-83J16.1 mediated URI1 and β-catenin signaling.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Oct;99:108010. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108010. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34358861
-
LncRNA PICSAR promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by sponging miRNA-4701-5p in rheumatoid arthritis.EBioMedicine. 2019 Dec;50:408-420. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.024. Epub 2019 Nov 30. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31791845 Free PMC article.
-
The p53 status in rheumatoid arthritis with focus on fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Immunol Res. 2021 Jun;69(3):225-238. doi: 10.1007/s12026-021-09202-7. Epub 2021 May 13. Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33983569 Review.
-
Regulation of Immune Responses and Chronic Inflammation by Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 19;10:1395. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01395. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31275325 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of miRNAs in Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy.Cells. 2023 Jun 30;12(13):1749. doi: 10.3390/cells12131749. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of lncRNAs in regulation of DKD and diabetes-related cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 13;12:1035487. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1035487. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36313695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarker profiling to determine clinical impact of microRNAs in cognitive disorders.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 9;14(1):8270. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58882-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38594359 Free PMC article.
-
Juanbi Qianggu Formula inhibits fibroblast-like synovicytes activation via repressing LncRNA ITSN1-2 to promote RIP2 K48 ubiquitination.Chin Med. 2025 Jul 8;20(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01164-4. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40629453 Free PMC article.
-
Applications and recent advances in transdermal drug delivery systems for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Nov;13(11):4417-4441. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.05.025. Epub 2023 May 26. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37969725 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang X, Feng H, Du J, Sun J, Li D, Hasegawa T, et al. . Aspirin promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation by blocking G0/G1 into S phase in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via downregulation of JAK/STAT3 and NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. (2018) 42:3135–48. 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3883 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

