Use of the JAK Inhibitor Ruxolitinib in the Treatment of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
- PMID: 33664745
- PMCID: PMC7923355
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.614704
Use of the JAK Inhibitor Ruxolitinib in the Treatment of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
Abstract
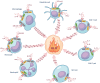
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rare hyperinflammatory syndrome driven by overactive T cells and macrophages that abundantly secrete numerous pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interferon (IFN)-gamma, interleukin (IL)-1-beta, IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, IL-18, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF). The release of these and other cytokines underlies many of the clinical and pathologic manifestations of HLH, which if left untreated, can lead to multi-organ failure and death. The advent of etoposide-based regimens, such as the Histiocyte Society HLH-94 and HLH-2004 protocols, has substantially decreased the mortality associated with HLH. Nevertheless, the 5-year survival remains low at ~60%. To improve upon these results, studies have focused on the use of novel cytokine-directed therapies to dampen inflammation in HLH. Among the agents being tested is ruxolitinib, a potent inhibitor of the Janus Kinase (JAK) and Signal Transducer and Activation of Transcription (STAT) pathway, which functions downstream of many HLH-associated cytokines. Here, we review the basic biology of HLH, including the role of cytokines in disease pathogenesis, and discuss the use of ruxolitinib in the treatment of HLH.
Keywords: Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; cytokine storm; inflammation; jak-stat; ruxolitinib.
Copyright © 2021 Keenan, Nichols and Albeituni.
Conflict of interest statement
KN receives research funding from Incyte Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

