Interleukin-18 and -10 may be associated with lymph node metastasis in breast cancer
- PMID: 33664817
- PMCID: PMC7882877
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2021.12515
Interleukin-18 and -10 may be associated with lymph node metastasis in breast cancer
Abstract
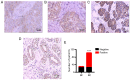
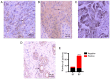
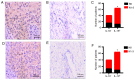
Reports on the expression of interleukin (IL)-10 in breast cancer are rare. The present study investigated the correlation between IL-18 and -10 in breast cancer, and assessed their clinical significance. Breast cancer (n=104) and breast fibroadenoma (n=31) tissues that were surgically removed and pathologically confirmed at Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University (Jinan, China) between November 2016 and January 2019 were collected. The expression of IL-18 and -10 was observed via immunohistochemistry. Breast cancer tissues were positive for IL-18 expression, which was primarily located in the cell membrane and cytoplasm. A significant difference in IL-18 expression was observed between breast cancer and fibroadenoma tissues (75.0 vs. 19.4%; P<0.001). IL-10 was expressed in breast cancer tissues and primarily located in the cytoplasm. Breast cancer tissues showed a significantly higher level of IL-10 expression compared with breast fibroadenoma tissues (78.8 vs. 22.6%; P<0.001). The regions of positive IL-18 and -10 expression were consistent. Tissues with positive expression of IL-18 and/or -10 had a significantly higher rate of lymph node metastasis than those with negative expression (IL-18: 67.9 vs. 42.3%; P=0.035; and IL-10: 67.1 vs. 40.9%; P=0.047). In conclusion, IL-18 is highly expressed in breast cancer and correlates positively with IL-10. Both IL-18 and -10 may correlate positively with lymph node metastasis in breast cancer.
Keywords: correlation analysis; immunohistochemistry; immunotherapy; lymph node metastasis.
Copyright: © Ma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association of chemotactic factor receptor 5 gene with breast cancer.Genet Mol Res. 2013 Nov 7;12(4):5289-300. doi: 10.4238/2013.November.7.4. Genet Mol Res. 2013. PMID: 24301790
-
Prospective study found that peripheral lymph node sampling reduced the false-negative rate of sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer.Chin J Cancer. 2016 Apr 4;35:35. doi: 10.1186/s40880-016-0099-x. Chin J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27044285 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonal-receptor positive breast cancer: IL-6 augments invasion and lymph node metastasis via stimulating cathepsin B expression.J Adv Res. 2016 Sep;7(5):661-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2016.06.007. Epub 2016 Jun 30. J Adv Res. 2016. PMID: 27482469 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression of adhesive molecule CD44v6 and p53 gene in breast cancer tissues and its relation with DNA ploidy].Ai Zheng. 2004 Nov;23(11 Suppl):1418-22. Ai Zheng. 2004. PMID: 15566648 Chinese.
-
POU5F1/Oct-4 expression in breast cancer tissue is significantly associated with non-sentinel lymph node metastasis.BMC Cancer. 2016 Mar 1;16:175. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1966-6. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26931354 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cytokine-mediated regulation of immune cell metabolic pathways in the tumor microenvironment.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 12. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04133-8. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40220026 Review.
-
Association of the IL-10 and IL-18 polymorphisms with nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 6;15:1543182. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1543182. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40115022 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the anti-neoplastic potential of Allium ascalonicum in averting the proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of triple-negative breast cancer through virtual docking and In Vitro approaches.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 7;25(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13796-8. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40055656 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone and OLT1177 Cooperate in the Reduction of Melanoma Growth by Inhibiting STAT3 Functions.Cells. 2023 Jan 12;12(2):294. doi: 10.3390/cells12020294. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36672229 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of a new prognostic signature based on cancer-associated fibroblast-driven genes in breast cancer.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Feb 6;12(4):700-720. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i4.700. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 38322675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nome ME, Euceda LR, Jabeen S, Debik J, Bathen TF, Giskeødegård GF, Taskén KA, Maelandsmo GM, Halvorsen B, Yndestad A, et al. Serum levels of inflammation-related markers and metabolites predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with and without bevacizumab in breast cancers. Int J Cancer. 2020;146:223–235. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32638. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang B, Zhu S, Song Q. New progress in immunotherapy for breast cancer. Herald Med. 2019;38:1013–1016.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
