Lactate-induced M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages promotes the invasion of pituitary adenoma by secreting CCL17
- PMID: 33664865
- PMCID: PMC7914368
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.53749
Lactate-induced M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages promotes the invasion of pituitary adenoma by secreting CCL17
Abstract
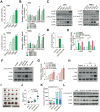
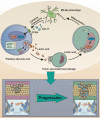
Background: Lactate greatly contributes to the regulation of intracellular communication within the tumor microenvironment (TME). However, the role of lactate in pituitary adenoma (PA) invasion is unclear. In this study, we aimed to clarify the effects of lactate on the TME and the effects of TME on PA invasion. Methods: To explore the correlation between TME acidosis and tumor invasion, LDHA and LAMP2 expression levels were quantified in invasive (n = 32) and noninvasive (n = 32) PA samples. The correlation between immune cell infiltration and tumor invasion was evaluated in 64 PAs. Critical chemokine and key signaling pathway components were detected by qPCR, Western blotting, siRNA knockdown, and specific inhibitors. The functional consequences of CCR4 signaling inhibition were evaluated in vitro and in vivo. Results: Lactate was positively associated with PA invasion. Of the 64 PA tissues, invasive PAs were related to high infiltration of M2-like tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) (P < 0.05). Moreover, lactate secreted from PA cells facilitated M2 polarization via the mTORC2 and ERK signaling pathways, while activated TAMs secreted CCL17 to promote PA invasion via the CCL17/CCR4/mTORC1 axis. According to univariate analysis of clinical data, high CCL17 expression was associated with larger tumor size (P = 0.0438), greater invasion (P = 0.0334), and higher susceptibility to postoperative recurrence (P = 0.0195) in human PAs. Conclusion: This study illustrates the dynamics between PA cells and immune TME in promoting PA invasion via M2 polarization. CCL17 levels in the TME are related to the PA invasiveness and clinical prognosis, and the CCL17/CCR4/mTOCR1 axis may serve as potential therapeutic targets for Pas.
Keywords: CCL17; lactate acid; mTOR; macrophages; pituitary adenoma.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





References
-
- Molitch ME. Diagnosis and Treatment of Pituitary Adenomas: A Review. JAMA. 2017;317:516–24. - PubMed
-
- Di Ieva A, Rotondo F, Syro LV, Cusimano MD, Kovacs K. Aggressive pituitary adenomas-diagnosis and emerging treatments. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10:423–35. - PubMed
-
- Ippolito L, Morandi A, Giannoni E, Chiarugi P. Lactate: A Metabolic Driver in the Tumour Landscape. Trends Biochem Sci. 2019;44:153–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

