SIRT3-mediated deacetylation of NLRC4 promotes inflammasome activation
- PMID: 33664876
- PMCID: PMC7914345
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.55573
SIRT3-mediated deacetylation of NLRC4 promotes inflammasome activation
Abstract
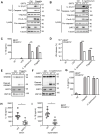
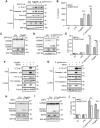
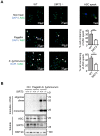
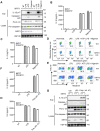
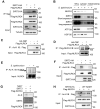
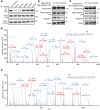
Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) infection of macrophage induces NLRC4 inflammasome-mediated production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β. Post-translational modifications on NLRC4 are critical for its activation. Sirtuin3 (SIRT3) is the most thoroughly studied mitochondrial nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) -dependent deacetylase. We wondered whether SIRT3 mediated-deacetylation could take part in NLRC4 inflammasome activation. Methods: We initially tested IL-1β production and pyroptosis after cytosolic transfection of flagellin or S. typhimurium infection in wild type and SIRT3-deficient primary peritoneal macrophages via immunoblotting and ELISA assay. These results were confirmed in SIRT3-deficient immortalized bone marrow derived macrophages (iBMDMs) which were generated by CRISPR-Cas9 technology. In addition, in vivo experiments were conducted to confirm the role of SIRT3 in S. typhimurium-induced cytokines production. Then NLRC4 assembly was analyzed by immune-fluorescence assay and ASC oligomerization assay. Immunoblotting, ELISA and flow cytometry were performed to clarify the role of SIRT3 in NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes activation. To further investigate the mechanism of SIRT3 in NLRC4 activation, co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), we did immunoblot, cellular fractionation and in-vitro deacetylation assay. Finally, to clarify the acetylation sites of NLRC4, we performed liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and immunoblotting analysis. Results: SIRT3 deficiency led to significantly impaired NLRC4 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis both in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, SIRT3 promotes NLRC4 inflammasome assembly by inducing more ASC speck formation and ASC oligomerization. However, SIRT3 is dispensable for NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasome activation. Moreover, SIRT3 interacts with and deacetylates NLRC4 to promote its activation. Finally, we proved that deacetylation of NLRC4 at Lys71 or Lys272 could promote its activation. Conclusions: Our study reveals that SIRT3 mediated-deacetylation of NLRC4 is pivotal for NLRC4 activation and the acetylation switch of NLRC4 may aid the clearance of S. typhimurium infection.
Keywords: NLRC4; S. typhimurium infection; SIRT3; deacetylation; inflammasome.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of NLRC4 is critical for inflammasome activation.Nature. 2012 Oct 25;490(7421):539-42. doi: 10.1038/nature11429. Epub 2012 Aug 12. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22885697
-
Atg16l2 augments Nlrc4 inflammasome activation by facilitating NAIPs-NLRC4 association.Eur J Immunol. 2024 Nov;54(11):e2451078. doi: 10.1002/eji.202451078. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Eur J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39175123
-
β-arrestin1 is critical for the full activation of NLRP3 and NLRC4 inflammasomes.J Immunol. 2015 Feb 15;194(4):1867-73. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401989. Epub 2015 Jan 12. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25582856
-
Advances in Understanding Activation and Function of the NLRC4 Inflammasome.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 21;22(3):1048. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031048. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33494299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of NLRC4 inflammasome in neurological disorders: Mechanisms, implications, and therapeutic potential.Pharmacol Ther. 2025 Mar;267:108803. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2025.108803. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39855275 Review.
Cited by
-
SIRT3 alleviates imiquimod-induced psoriatic dermatitis through deacetylation of XBP1s and modulation of TLR7/8 inducing IL-23 production in macrophages.Front Immunol. 2023 May 19;14:1128543. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1128543. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37275851 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on the differentiation potential of primary stem cells: a systematic review.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Apr 11;14(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03324-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37038234 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated SIRT3 Parkin-dependently activates cell mitophagy to ameliorate TNF-α-induced psoriasis-related phenotypes in HaCaT cells through deacetylating FOXO3a for its activation.Arch Dermatol Res. 2023 May;315(4):847-857. doi: 10.1007/s00403-022-02453-w. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023. PMID: 36352150
-
Targeting pyroptosis in myocardial inflammation and fibrosis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Apoptosis. 2025 Jul 23. doi: 10.1007/s10495-025-02151-8. Online ahead of print. Apoptosis. 2025. PMID: 40702245 Review.
-
Acetylation in Tumor Immune Evasion Regulation.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 22;12:771588. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.771588. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34880761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM. Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes. Cell. 2014;157:1013–22. - PubMed
-
- Poyet JL, Srinivasula SM, Tnani M, Razmara M, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES. Identification of Ipaf, a human caspase-1-activating protein related to Apaf-1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:28309–13. - PubMed
-
- Ren J, Sang Y, Tan Y, Tao J, Ni J, Liu S. et al. Acetylation of lysine 201 inhibits the DNA-binding ability of PhoP to regulate Salmonella virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:https. //doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1005458. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Franchi L, Amer A, Body-Malapel M, Kanneganti TD, Ozoren N, Jagirdar R. et al. Cytosolic flagellin requires Ipaf for activation of caspase-1 and interleukin 1beta in salmonella-infected macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:576–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

