SIRT3-mediated deacetylation of NLRC4 promotes inflammasome activation
- PMID: 33664876
- PMCID: PMC7914345
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.55573
SIRT3-mediated deacetylation of NLRC4 promotes inflammasome activation
Abstract
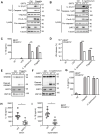
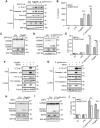
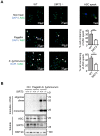
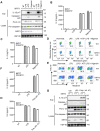
Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) infection of macrophage induces NLRC4 inflammasome-mediated production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β. Post-translational modifications on NLRC4 are critical for its activation. Sirtuin3 (SIRT3) is the most thoroughly studied mitochondrial nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) -dependent deacetylase. We wondered whether SIRT3 mediated-deacetylation could take part in NLRC4 inflammasome activation. Methods: We initially tested IL-1β production and pyroptosis after cytosolic transfection of flagellin or S. typhimurium infection in wild type and SIRT3-deficient primary peritoneal macrophages via immunoblotting and ELISA assay. These results were confirmed in SIRT3-deficient immortalized bone marrow derived macrophages (iBMDMs) which were generated by CRISPR-Cas9 technology. In addition, in vivo experiments were conducted to confirm the role of SIRT3 in S. typhimurium-induced cytokines production. Then NLRC4 assembly was analyzed by immune-fluorescence assay and ASC oligomerization assay. Immunoblotting, ELISA and flow cytometry were performed to clarify the role of SIRT3 in NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes activation. To further investigate the mechanism of SIRT3 in NLRC4 activation, co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), we did immunoblot, cellular fractionation and in-vitro deacetylation assay. Finally, to clarify the acetylation sites of NLRC4, we performed liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and immunoblotting analysis. Results: SIRT3 deficiency led to significantly impaired NLRC4 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis both in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, SIRT3 promotes NLRC4 inflammasome assembly by inducing more ASC speck formation and ASC oligomerization. However, SIRT3 is dispensable for NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasome activation. Moreover, SIRT3 interacts with and deacetylates NLRC4 to promote its activation. Finally, we proved that deacetylation of NLRC4 at Lys71 or Lys272 could promote its activation. Conclusions: Our study reveals that SIRT3 mediated-deacetylation of NLRC4 is pivotal for NLRC4 activation and the acetylation switch of NLRC4 may aid the clearance of S. typhimurium infection.
Keywords: NLRC4; S. typhimurium infection; SIRT3; deacetylation; inflammasome.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
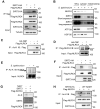
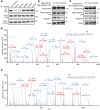
References
-
- Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM. Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes. Cell. 2014;157:1013–22. - PubMed
-
- Poyet JL, Srinivasula SM, Tnani M, Razmara M, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES. Identification of Ipaf, a human caspase-1-activating protein related to Apaf-1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:28309–13. - PubMed
-
- Ren J, Sang Y, Tan Y, Tao J, Ni J, Liu S. et al. Acetylation of lysine 201 inhibits the DNA-binding ability of PhoP to regulate Salmonella virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:https. //doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1005458. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Franchi L, Amer A, Body-Malapel M, Kanneganti TD, Ozoren N, Jagirdar R. et al. Cytosolic flagellin requires Ipaf for activation of caspase-1 and interleukin 1beta in salmonella-infected macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:576–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

