Proton beam therapy for a giant hepatic hemangioma: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 33665385
- PMCID: PMC7902997
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctro.2021.01.014
Proton beam therapy for a giant hepatic hemangioma: A case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Hepatic hemangiomas are benign tumors with a favorable prognosis, but giant hepatic hemangiomas can cause abdominal symptoms and are indicated for treatment. Most cases are treated with surgery, but radiotherapy has also been used. However, to date, there have been no reports of proton beam therapy for a hepatic hemangioma.
Case presentation: A 46-year-old woman had a tumor of 80 × 80 mm in the left medial lobe of the liver, which was diagnosed as a giant hemangioma based on the contrast pattern. Therapy was required for a giant hepatic hemangioma with symptoms, but the patient refused blood transfusion due to religious reasons, which made surgical resection difficult. Therefore, she was referred to our hospital for proton beam therapy. At her first visit, liver function was Child-Pugh A (5 points) and there was no elevation of tumor markers. Proton beam therapy of 28.6 Gy (RBE) given in 13 fractions was performed without interruption. The only observed acute radiation toxicity was Grade 1 dermatitis. One year after proton beam therapy, the hemangioma had significantly decreased, and a complete response has been maintained for 15 years based on ultrasound and MRI.
Conclusion: This case is the first reported use of proton beam therapy for a hepatic hemangioma. The outcome suggests that this treatment may be effective for a giant liver hemangioma.
Keywords: Hemangioma; Liver; Proton beam therapy; Radiotherapy; Secondary cancer.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
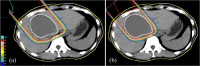
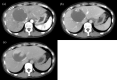

References
-
- Ishak K.G., Rabin L. Benign tumors of the liver. Med Clin North Am. 1975;59:995–1013. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z., Tan H., Liu X., Sun Y. Extremely giant liver hemangioma (50 cm) with Kasabach-Merritt syndrome. J Gastrointest Surg. 2017;21:1748–1749. - PubMed
-
- Reddy K.R., Kligerman S., Levi J., Livingstone A., Molina E., Franceschi D. Benign and solid tumors of the liver: relationship to sex, age, size of tumors, and outcome. Am Surg. 2001;67:173–178. - PubMed
-
- Hasan H.Y., Hinshaw J.L., Borman E.J., Gegios A., Leverson G., Winslow E.R. Assessing normal growth of hepatic hemangiomas during long-term follow-up. JAMA Surg. 2014;149:1266–1271. - PubMed
-
- Bioulac-Sage P., Laumonier H., Laurent C., Blanc J., Balabaud C. Benign and malignant vasculartumors of the liver in adults. Semin Liver Dis. 2008;28:302–314. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

