Effects of ertugliflozin on kidney composite outcomes, renal function and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an analysis from the randomised VERTIS CV trial
- PMID: 33665685
- PMCID: PMC8099851
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-021-05407-5
Effects of ertugliflozin on kidney composite outcomes, renal function and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an analysis from the randomised VERTIS CV trial
Abstract
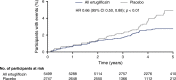
Aims/hypothesis: In previous work, we reported the HR for the risk (95% CI) of the secondary kidney composite endpoint (time to first event of doubling of serum creatinine from baseline, renal dialysis/transplant or renal death) with ertugliflozin compared with placebo as 0.81 (0.63, 1.04). The effect of ertugliflozin on exploratory kidney-related outcomes was evaluated using data from the eValuation of ERTugliflozin effIcacy and Safety CardioVascular outcomes (VERTIS CV) trial (NCT01986881).
Methods: Individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established atherosclerotic CVD were randomised to receive ertugliflozin 5 mg or 15 mg (observations from both doses were pooled), or matching placebo, added on to existing treatment. The kidney composite outcome in VERTIS CV (reported previously) was time to first event of doubling of serum creatinine from baseline, renal dialysis/transplant or renal death. The pre-specified exploratory composite outcome replaced doubling of serum creatinine with sustained 40% decrease from baseline in eGFR. In addition, the impact of ertugliflozin on urinary albumin/creatinine ratio (UACR) and eGFR over time was assessed.
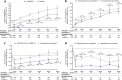
Results: A total of 8246 individuals were randomised and followed for a mean of 3.5 years. The exploratory kidney composite outcome of sustained 40% reduction from baseline in eGFR, chronic kidney dialysis/transplant or renal death occurred at a lower event rate (events per 1000 person-years) in the ertugliflozin group than with the placebo group (6.0 vs 9.0); the HR (95% CI) was 0.66 (0.50, 0.88). At 60 months, in the ertugliflozin group, placebo-corrected changes from baseline (95% CIs) in UACR and eGFR were -16.2% (-23.9, -7.6) and 2.6 ml min-1 [1.73 m]-2 (1.5, 3.6), respectively. Ertugliflozin was associated with a consistent decrease in UACR and attenuation of eGFR decline across subgroups, with a suggested larger effect observed in the macroalbuminuria and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease (KDIGO CKD) high/very high-risk subgroups.
Conclusions/interpretation: Among individuals with type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic CVD, ertugliflozin reduced the risk for the pre-specified exploratory composite renal endpoint and was associated with preservation of eGFR and reduced UACR.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01986881.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Diabetic nephropathies; Ertugliflozin; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

