Glial insulin regulates cooperative or antagonistic Golden goal/Flamingo interactions during photoreceptor axon guidance
- PMID: 33666170
- PMCID: PMC7987344
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.66718
Glial insulin regulates cooperative or antagonistic Golden goal/Flamingo interactions during photoreceptor axon guidance
Abstract
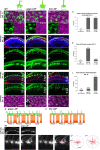
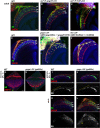
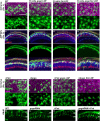
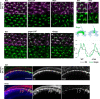
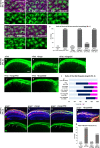
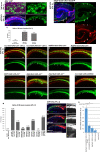
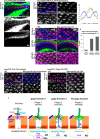
Transmembrane protein Golden goal (Gogo) interacts with atypical cadherin Flamingo (Fmi) to direct R8 photoreceptor axons in the Drosophila visual system. However, the precise mechanisms underlying Gogo regulation during columnar- and layer-specific R8 axon targeting are unknown. Our studies demonstrated that the insulin secreted from surface and cortex glia switches the phosphorylation status of Gogo, thereby regulating its two distinct functions. Non-phosphorylated Gogo mediates the initial recognition of the glial protrusion in the center of the medulla column, whereas phosphorylated Gogo suppresses radial filopodia extension by counteracting Flamingo to maintain a one axon-to-one column ratio. Later, Gogo expression ceases during the midpupal stage, thus allowing R8 filopodia to extend vertically into the M3 layer. These results demonstrate that the long- and short-range signaling between the glia and R8 axon growth cones regulates growth cone dynamics in a stepwise manner, and thus shapes the entire organization of the visual system.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Drosophila; axon guidance; cell-cell communication; developmental biology; developmental neurobiology; gogo receptor; neuroscience; visual system.
© 2021, Takechi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
HT, SH, YN, YI, RI, MS, AS, TS No competing interests declared
Figures








Similar articles
-
Golden Goal collaborates with Flamingo in conferring synaptic-layer specificity in the visual system.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Mar;14(3):314-23. doi: 10.1038/nn.2756. Epub 2011 Feb 13. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21317905
-
The transmembrane protein Golden goal regulates R8 photoreceptor axon-axon and axon-target interactions.Neuron. 2008 Mar 13;57(5):691-704. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.012. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18341990
-
Orthodenticle Is Required for the Expression of Principal Recognition Molecules That Control Axon Targeting in the Drosophila Retina.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jun 26;11(6):e1005303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005303. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26114289 Free PMC article.
-
Axon targeting in the Drosophila visual system.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003 Feb;13(1):90-5. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(03)00004-7. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 12593986 Review.
-
Cell surface control of the layer specific targeting in the Drosophila visual system.Genes Genet Syst. 2014;89(1):9-15. doi: 10.1266/ggs.89.9. Genes Genet Syst. 2014. PMID: 24817757 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of axon pathfinding by astroglia across genetic model organisms.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Oct 24;17:1241957. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1241957. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37941606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cytoplasmic LIM Domain Protein Espinas Contributes to Photoreceptor Layer Selection in the Visual System.Biology (Basel). 2020 Dec 14;9(12):466. doi: 10.3390/biology9120466. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33327397 Free PMC article.
-
Flamingo participates in multiple models of cell competition.Elife. 2024 Dec 30;13:RP98535. doi: 10.7554/eLife.98535. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39854621 Free PMC article.
-
Cell adhesion and actin dynamics factors promote axonal extension and synapse formation in transplanted Drosophila photoreceptor cells.Dev Growth Differ. 2024 Apr;66(3):205-218. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12916. Epub 2024 Feb 25. Dev Growth Differ. 2024. PMID: 38403285 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonal gatekeeping via the blood-brain barrier governs caste-specific behavior in ants.Cell. 2023 Sep 28;186(20):4289-4309.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.08.002. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Cell. 2023. PMID: 37683635 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

