General principles of image optimization in EUS
- PMID: 33666178
- PMCID: PMC8248305
- DOI: 10.4103/eus.eus_80_20
General principles of image optimization in EUS
Abstract
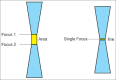
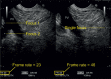
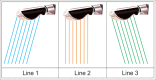
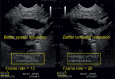
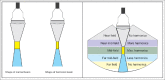
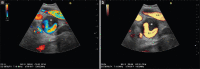
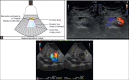
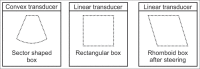
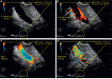
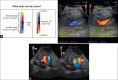
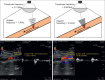
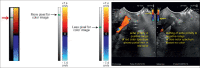
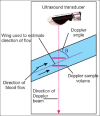
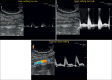
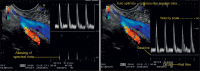
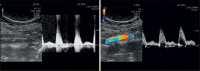
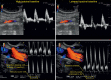
With the development of modern EUS, multiple imaging functions, transducer settings, and examination modes have become available for clinical settings. While the major determinants of the ultrasound beam are still comprised of the signal wavelength, its frequency range, and its amplitude, other modifications and calculations have gained more interest for advanced users, such as tissue harmonic imaging (THI), spatial and frequency compounding, certain versions of speckle reduction, and various Doppler/duplex settings. The goal of such techniques is a better, perhaps more realistic image, with reduced artifacts (such as speckle), better image contrast, and an improved signal-to-noise ratio. In addition, "add-ons" such as THI, which is based on the phenomenon of nonlinear distortion of acoustic signals as they travel through tissues, provide greater contrast and an enhanced spatial resolution than conventional EUS. Finally, optimization of spectral and color Doppler imaging in EUS requires experience and knowledge about the basic principles of Doppler/duplex phenomena. For these purposes, factors such as adjustment of Doppler controls, Doppler angle, color gain, spectral wall filters, and others require special attention during EUS examinations. Incorporating these advanced techniques in EUS examinations may be time-consuming and cumbersome. Hence, practical guidelines enabling endosonographers to steer safely through the large quantity of technological properties and settings (knobology) are appreciated. This review provides an overview of the role of important imaging features to be adjusted before, during, and after EUS procedures.
Keywords: B-mode; EUS; doppler; guideline; image quality.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
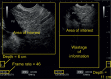
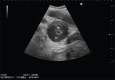
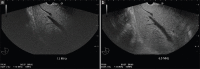
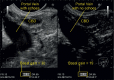
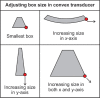
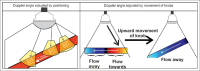

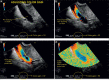
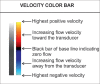


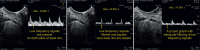
References
-
- Dietrich CF, Bartsch L, Turco V, et al. Knöpfologie in der B-Bild-Sonografie. Gastroenterologie up 2date. 2018;14:347–64.
-
- Ishikawa H, Hirooka Y, Itoh A, et al. A comparison of image quality between tissue harmonic imaging and fundamental imaging with an electronic radial scanning echoendoscope in the diagnosis of pancreatic diseases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;57:931–6. - PubMed
-
- Ohno E, Kawashima H, Hashimoto S, et al. Current status of tissue harmonic imaging in endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) and EUS-elastography in pancreatobiliary diseases. Dig Endosc. 2015;27(Suppl 1):68–73. - PubMed
-
- Bang JY, Hawes RH, Varadarajulu S. Objective evaluation of a new endoscopic ultrasound processor. Dig Endosc. 2013;25:554–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

