How varying parameters impact insecticide resistance bioassay: An example on the worldwide invasive pest Drosophila suzukii
- PMID: 33667239
- PMCID: PMC7935283
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247756
How varying parameters impact insecticide resistance bioassay: An example on the worldwide invasive pest Drosophila suzukii
Abstract
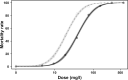
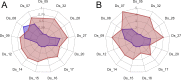
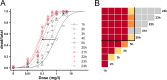
Monitoring pesticide resistance is essential for effective and sustainable agricultural practices. Bioassays are the basis for pesticide-resistance testing, but devising a reliable and reproducible method can be challenging because these tests are carried out on living organisms. Here, we investigated five critical parameters and how they affected the evaluation of resistance to the organophosphate phosmet or the pyrethroid lambda-cyhalothrin using a tarsal-contact protocol on Drosophila suzukii, a worldwide invasive pest. Three of the parameters were related to insect biology: (i) sex, (ii) age of the imago (adult stage) and (iii) genetic diversity of the tested population. The two remaining parameters were linked to the experimental setup: (iv) the number of individuals tested per dose and (v) the duration of exposure to the active ingredient. Results showed that response to insecticide differed depending on sex, males being twice as susceptible to phosmet as females. Age principally affected young females' susceptibility to phosmet, because 0-24 hour-old flies were twice as susceptible as 24-48 hour-old and 72-96 hour-old females. Genetic diversity had no observable effect on resistance levels. The precision and accuracy of the median lethal dose (LD50) were greatly affected by the number of individuals tested per dose with a threshold effect. Finally, optimal duration of exposure to the active ingredient was 24 h, as we found an underestimation of mortality when assessed between 1 and 5 h after exposure to lambda-cyhalothrin. None of the main known point mutations on the para sodium channel gene associated with a knockdown effect were observed. Our study demonstrates the importance of calibrating the various parameters of a bioassay to develop a reliable method. It also provides a valuable and transferable protocol for monitoring D. suzukii resistance worldwide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Cotter SC, Simpson SJ, Raubenheimer D, Wilson K. Macronutrient balance mediates trade‐offs between immune function and life history traits. Functional Ecology. 2010;25(1):186–98.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

