Quinoline Functionalized Schiff Base Silver (I) Complexes: Interactions with Biomolecules and In Vitro Cytotoxicity, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities
- PMID: 33668169
- PMCID: PMC7956476
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26051205
Quinoline Functionalized Schiff Base Silver (I) Complexes: Interactions with Biomolecules and In Vitro Cytotoxicity, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities
Abstract
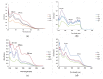
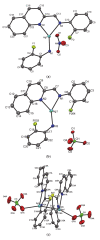
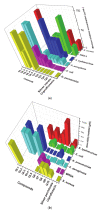
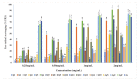
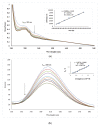
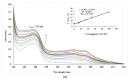
A series of fifteen silver (I) quinoline complexes Q1-Q15 have been synthesized and studied for their biological activities. Q1-Q15 were synthesized from the reactions of quinolinyl Schiff base derivatives L1-L5 (obtained by condensing 2-quinolinecarboxaldehyde with various aniline derivatives) with AgNO3, AgClO4 and AgCF3SO3. Q1-Q15 were characterized by various spectroscopic techniques and the structures of [Ag(L1)2]NO3Q1, [Ag(L1)2]ClO4Q6, [Ag(L2)2]ClO4Q7, [Ag(L2)2]CF3SO3Q12 and [Ag(L4)2]CF3SO3Q14 were unequivocally determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. In vitro antimicrobial tests against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria revealed the influence of structure and anion on the complexes' moderate to excellent antibacterial activity. In vitro antioxidant activities of the complexes showed their good radical scavenging activity in ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP). Complexes with the fluorine substituent or the thiophene or benzothiazole moieties are more potent with IC50 between 0.95 and 2.22 mg/mL than the standard used, ascorbic acid (2.68 mg/mL). The compounds showed a strong binding affinity with calf thymus-DNA via an intercalation mode and protein through a static quenching mechanism. Cytotoxicity activity was examined against three carcinoma cell lines (HELA, MDA-MB231, and SHSY5Y). [Ag(L2)2]ClO4Q7 with a benzothiazole moiety and [Ag(L4)2]ClO4Q9 with a methyl substituent had excellent cytotoxicity against HELA cells.
Keywords: Ag(I); BSA; CT-DNA; antimicrobial; antioxidant; cytotoxicity; quinolines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Aryl variation and anion effect on CT-DNA binding and in vitro biological studies of pyridinyl Ag(I) complexes.J Inorg Biochem. 2021 Jan;214:111266. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2020.111266. Epub 2020 Oct 5. J Inorg Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33166866
-
New penta-Coordinated Cadmium(II) Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization, Thermal, Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Cytotoxicity Properties.Chem Biodivers. 2024 May;21(5):e202301667. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202301667. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Chem Biodivers. 2024. PMID: 38502834
-
Structures and biochemical evaluation of silver(I) 5,5-diethylbarbiturate complexes with bis(diphenylphosphino)alkanes as potential antimicrobial and anticancer agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Oct 20;139:901-916. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.08.062. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28881285
-
Versatile applications of transition metal incorporating quinoline Schiff base metal complexes: An overview.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Oct 5;258:115549. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115549. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37321110 Review.
-
An Insight into the Effect of Schiff Base and their d and f Block Metal Complexes on Various Cancer Cell Lines as Anticancer Agents: A Review.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(7):488-503. doi: 10.2174/0118715206280314231201111358. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38279753 Review.
Cited by
-
Ni2+ and Cu2+ complexes of N-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-N-mesityl formamidine dithiocarbamate structural and functional properties as CYP3A4 potential substrates.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 17;13(1):13414. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39502-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37591990 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization, and nonlinear optical properties of copper (II) ligand Schiff base complexes derived from 3-Nitrobenzohydrazide and benzyl.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 7;13(1):10988. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38086-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37420025 Free PMC article.
-
Different Schiff Bases-Structure, Importance and Classification.Molecules. 2022 Jan 25;27(3):787. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030787. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and Spectroscopic Investigations of Schiff Base Ligand and Its Bimetallic Ag(I) Complex as DNA and BSA Binders.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 2;11(10):1449. doi: 10.3390/biom11101449. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34680081 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Coordination Chemistry of Schiff Base Complexes: A Journey from Nanoarchitectonic Design to Biomedical Applications.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2025 Feb 3;383(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s41061-025-00489-w. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2025. PMID: 39900838 Review.
References
-
- Bine F.K., Nkungli N.K., Numbonui T.S., Numbonui Ghogomu J. Structural Properties and Reactive Site Selectivity of Some Transition Metal Complexes of 2,2’(1E,1’E)-(ethane-1,2-diylbis(azan-1-yl-1-ylidene))bis(phenylmethan-1-yl-1-yli dene)dibenzoic Acid: DFT, Conceptual DFT, QTAIM, and MEP Studies. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018;2018:4510648. doi: 10.1155/2018/4510648. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khandar A.A., Afkhami F.A., Hosseini-Yazdi S.A., White J.M., Kassel S., Dougherty W.G., Lipkowski J., van Derveer D., Giester G., Costantino F. Anion influence in the structural diversity of cadmium coordination polymers constructed from a pyridine based Schiff base ligand. Inorg. Chim. Acta. 2015;427:87–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2014.11.028. - DOI
-
- Kajal A., Bala S., Kamboj S., Sharma N., Saini V. Schiff Bases: A Versatile Pharmacophore. J. Catal. 2013;2013:1–14. doi: 10.1155/2013/893512. - DOI
-
- Garrido Montalban A. Quinolines and Isoquinolines. Heterocycl. Nat. Prod. Synth. 2011:299–339. doi: 10.1002/9783527634880.ch9. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

