Unraveling the Gut Microbiome of the Invasive Small Indian Mongoose (Urva auropunctata) in the Caribbean
- PMID: 33668312
- PMCID: PMC7996244
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9030465
Unraveling the Gut Microbiome of the Invasive Small Indian Mongoose (Urva auropunctata) in the Caribbean
Abstract
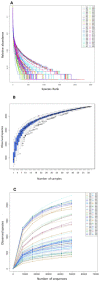
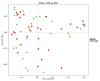
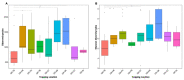
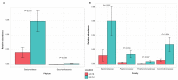
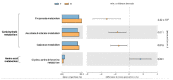
Small Indian mongooses (Urva auropunctata) are among the most pervasive predators to disrupt the native ecology on Caribbean islands and are strongly entrenched in their areas of introduction. Few studies, however, have considered the microbial ecology of such biological invasions. In this study, we investigated the gut microbiota of invasive small Indian mongooses in terms of taxonomic diversity and functional potential. To this end, we collected fecal samples from 60 free-roaming mongooses trapped in different vegetation zones on the island Saint Kitts. The core gut microbiome, assessed by 16S rRNA amplicon gene sequencing on the Ion S5TM XL platform, reflects a carnivore-like signature with a dominant abundance of Firmicutes (54.96%), followed by Proteobacteria (13.98%) and Fusobacteria (12.39%), and a relatively minor contribution of Actinobacteria (10.4%) and Bacteroidetes (6.40%). Mongooses trapped at coastal sites exhibited a higher relative abundance of Fusobacterium spp. whereas those trapped in scrubland areas were enriched in Bacteroidetes, but there was no site-specific difference in predicted metabolic properties. Between males and females, beta-diversity was not significantly different and no sex-specific strategies for energy production were observed. However, the relative abundance of Gammaproteobacteria, and more specifically, Enterobacteriaceae, was significantly higher in males. This first description of the microbial profile of small Indian mongooses provides new insights into their bioecology and can serve as a springboard to further elucidating this invasive predator's impact throughout the Caribbean.
Keywords: Caribbean; Herpestes; Urva auropunctata; carnivore; gut microbiota; invasive species; microbial profiling; small Indian mongoose.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
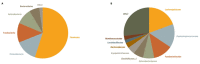


References
-
- West A.G., Waite D.W., Deines P., Bourne D.G., Digby A., Mckenzie V.J., Taylor M.W. The microbiome in threatened species conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2019;229:85–98. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2018.11.016. - DOI
-
- Global Invasive Species Database. [(accessed on 29 April 2020)];2020 Available online: http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/100_worst.php.
-
- Veron G., Patou M.L., Pothet G., Simberloff D., Jennings A.P. Systematic status and biogeography of the Javan and small Indian mongooses (Herpestidae, Carnivora) Zool. Scr. 2007;36:1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-6409.2006.00261.x. - DOI
-
- Horst G.R., Hoagland D.B., Kilpatrick C.W. Biogeography of the West Indies: Patterns and Perspectives. 2nd ed. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2001. The mongoose in the West Indies: The biogeography and population biology of an introduced species; pp. 409–424. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

