Critical Review of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles as Carriers of Neuroprotective Drugs and Extracts
- PMID: 33668341
- PMCID: PMC7996241
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11030563
Critical Review of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles as Carriers of Neuroprotective Drugs and Extracts
Abstract
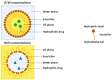
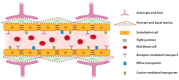
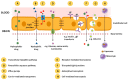
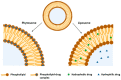
The biggest obstacle to the treatment of diseases that affect the central nervous system (CNS) is the passage of drugs across the blood-brain barrier (BBB), a physical barrier that regulates the entry of substances into the brain and ensures the homeostasis of the CNS. This review summarizes current research on lipid-based nanoparticles for the nanoencapsulation of neuroprotective compounds. A survey of studies on nanoemulsions (NEs), nanoliposomes/nanophytosomes and solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs)/nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) was carried out and is discussed herein, with particular emphasis upon their unique characteristics, the most important parameters influencing the formulation of each one, and examples of neuroprotective compounds/extracts nanoencapsulated using these nanoparticles. Gastrointestinal absorption is also discussed, as it may pose some obstacles for the absorption of free and nanoencapsulated neuroprotective compounds into the bloodstream, consequently hampering drug concentration in the brain. The transport mechanisms through which compounds or nanoparticles may cross BBB into the brain parenchyma, and the potential to increase drug bioavailability, are also discussed. Additionally, factors contributing to BBB disruption and neurodegeneration are described. Finally, the advantages of, and obstacles to, conventional and unconventional routes of administration to deliver nanoencapsulated neuroprotective drugs to the brain are also discussed, taking into account the avoidance of first-pass metabolism, onset of action, ability to bypass the BBB and concentration of the drug in the brain.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; lipids; nanoemulsions; nanoliposomes; nanoparticles; nanophytosomes; nanostructured lipid carriers; natural products; solid lipid nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipid nanoparticles strategies to modify pharmacokinetics of central nervous system targeting drugs: Crossing or circumventing the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to manage neurological disorders.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Oct;189:114485. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114485. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35970274 Review.
-
Intranasal delivery of nanostructured lipid carriers, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanoemulsions: A current overview of in vivo studies.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Apr;11(4):925-940. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.012. Epub 2021 Mar 13. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 33996407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as New Generations of Blood-Brain Barrier Transmitters.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021 Dec 15;12(24):4475-4490. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00540. Epub 2021 Nov 27. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34841846 Review.
-
Navigating the Nose-to-Brain Route: A Systematic Review on Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for Central Nervous System Disorders.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Feb 27;16(3):329. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16030329. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38543223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as Smart Drug Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Glioblastoma Multiforme.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Sep 10;12(9):860. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12090860. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32927610 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nano-Lipids Based on Ginger Oil and Lecithin as a Potential Drug Delivery System.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 9;14(8):1654. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081654. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015280 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the anti-aging effects of active components of Artemia franciscana loaded in hyalurosome.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 8;15(1):1293. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83731-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39779758 Free PMC article.
-
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs): An Advanced Drug Delivery System Targeting Brain through BBB.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 31;13(8):1183. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081183. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The therapeutic potential of nanoencapsulated anti-inflammatory drugs delivered to the gut.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025 Mar;20(6):539-541. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2025.2457321. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39905975 No abstract available.
-
Role of Nanomedicine in Transforming Pharmacotherapy for Substance Use Disorder (SUD).Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2025 Mar-Apr;17(2):e70008. doi: 10.1002/wnan.70008. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40190158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Assadpour E., Jafari S.M. Chapter One—An overview of lipid-based nanostructures for encapsulation of food ingredients. In: Jafari S.M., editor. Lipid-Based Nanostructures for Food Encapsulation Purposes. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2019. pp. 1–34.
-
- Jafari S.M. In: Nanoencapsulation Technologies for the Food and Nutraceutical Industries. Jafari S.M., editor. Academic Press; London, UK: 2016.
-
- Quintanilla-Carvajal M.X., Camacho-Díaz B.H., Meraz-Torres L.S., Chanona-Pérez J.J., Alamilla-Beltrán L., Jimenéz-Aparicio A., Gutiérrez-López G.F. Nanoencapsulation: A new trend in food engineering processing. Food Eng. Rev. 2010;2:39–50. doi: 10.1007/s12393-009-9012-6. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

