From Fish Waste to Value: An Overview of the Sustainable Recovery of Omega-3 for Food Supplements
- PMID: 33668684
- PMCID: PMC7918619
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26041002
From Fish Waste to Value: An Overview of the Sustainable Recovery of Omega-3 for Food Supplements
Abstract
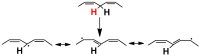
The disposal of food waste is a current and pressing issue, urging novel solutions to implement sustainable waste management practices. Fish leftovers and their processing byproducts represent a significant portion of the original fish, and their disposal has a high environmental and economic impact. The utilization of waste as raw materials for the production of different classes of biofuels and high-value chemicals, a concept known as "biorefinery", is gaining interest in a vision of circular economy and zero waste policies. In this context, an interesting route of valorization is the extraction of omega-3 fatty acids (ω-3 FAs) for nutraceutical application. These fatty acids, such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) have received attention over the last decades due to their beneficial effects on human health. Their sustainable production is a key process for matching the increased market demand while reducing the pressure on marine ecosystems and lowering the impact of waste production. The high resale value of the products makes this waste a powerful tool that simultaneously protects the environment and benefits the global economy. This review aims to provide a complete overview of the sustainable exploitation of fish waste to recover ω-3 FAs for food supplement applications, covering composition, storage, and processing of the raw material.
Keywords: DHA; EPA; PUFA; biorefinery; fish oil extraction; fish waste; omega-3; supercritical fluid extraction; supplements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Fiori L., Volpe M., Lucian M., Anesi A., Manfrini M., Guella G. From Fish Waste to Omega-3 Concentrates in a Biorefinery Concept. Waste Biomass Valorization. 2017;8:2609–2620. doi: 10.1007/s12649-017-9893-1. - DOI
-
- Kratky L., Zamazal P. Economic feasibility and sensitivity analysis of fish waste processing biorefinery. J. Clean. Prod. 2020;243:118677. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118677. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

