Room Temperature Nanoencapsulation of Bioactive Eicosapentaenoic Acid Rich Oil within Whey Protein Microparticles
- PMID: 33668857
- PMCID: PMC7996356
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11030575
Room Temperature Nanoencapsulation of Bioactive Eicosapentaenoic Acid Rich Oil within Whey Protein Microparticles
Abstract
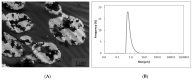
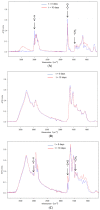
In this study, emulsion electrospraying assisted by pressurized gas (EAPG) has been performed for the first time to entrap ca. 760 nm droplets of the bioactive eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)-rich oil into whey protein concentrate (WPC) at room temperature. The submicron droplets of EPA oil were encapsulated within WPC spherical microparticles, with sizes around 5 µm. The EPA oil did not oxidize in the course of the encapsulation performed at 25 °C and in the presence of air, as corroborated by the peroxide value measurements. Attenuated Total Reflection-Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy and oxygen consumption tests confirmed that the encapsulated EPA-rich oil showed increased oxidative stability in comparison with the free oil during an accelerated oxidation test under ultraviolet light. Moreover, the encapsulated EPA-rich oil showed increased thermal stability in comparison with the free oil, as measured by oxidative thermogravimetric analysis. The encapsulated EPA-rich oil showed a somewhat reduced organoleptic impact in contrast with the neat EPA oil using rehydrated powdered milk as a reference. Finally, the oxidative stability by thermogravimetric analysis and organoleptic impact of mixtures of EPA and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)-loaded microparticles was also studied, suggesting an overall reduced organoleptic impact compared to pure EPA. The results here suggest that it is possible to encapsulate 80% polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)-enriched oils by emulsion EAPG technology at room temperature, which could be used to produce personalized nutraceuticals or pharmaceuticals alone or in combination with other microparticles encapsulating different PUFAs to obtain different targeted health and organoleptic benefits.
Keywords: EPA-rich oil; WPC microparticles; electrospraying; encapsulation; oxidative and thermal stability; personalized nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest regarding this manuscript.
Figures







References
-
- Panse M.L., Phalke S.D. Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2016. World Market of Omega-3 Fatty Acids; pp. 79–88.
-
- GOED Omega 3, Council for Responsible Nutrition. Oxidation in Omega-3 Oils: An Overview. [(accessed on 24 February 2021)];2015 Available online: https://goedomega3.com/storage/app/media/scientific-reports/Oxidation%20....
-
- Kaushik P., Dowling K., Barrow C.J., Adhikari B. Microencapsulation of omega-3 fatty acids: A review of microencapsulation and characterization methods. J. Funct. Foods. 2015;19:868–881. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2014.06.029. - DOI
-
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and brain, eye and nerve development (ID 501, 513, 540), maintenance of normal brain function (ID 497, 501, 510, 513, 519, 521, 534, 540, 688, 1323, 1360, 4294), maintenance of normal vision (ID 508, 510, 513, 519, 529, 540, 688, 2905, 4294), maintenance of normal cardiac function (ID 510, 688, 1360), “maternal health; pregnancy and nursing” (ID 514), “to fulfil increased omega-3 fatty acids need during pregnancy” (ID 539), “skin and digestive tract epithelial cells maintenance” (ID 525), enhancement of mood (ID 536), “membranes cell structure” (ID 4295), “anti-inflammatory action” (ID 4688) and maintenance of normal blood LDL-cholesterol concentrations (ID 4719) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011;9:2224. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2224. - DOI
Grants and funding
- RTI-2018-097249B-C1/Spanish Ministry of Science and Universities
- H2020 EU FODIAC project (reference number 778388)/European Union H2020
- H2020 EU 554 CAPSULTEK project (reference number 873827),/European Union H2020
- CDTI-CIEN DANTIAN project (IDI-20190954)/CDTI
- CYTED thematic network (code 319RT0576)/Cyted
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

