Evaluation of Triclosan Effects on Cultured Swine Luteal Cells
- PMID: 33668891
- PMCID: PMC7996528
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11030606
Evaluation of Triclosan Effects on Cultured Swine Luteal Cells
Abstract
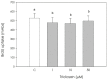
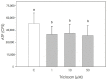
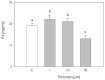
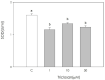
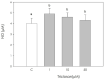
Triclosan is a chlorinated phenolic, used in many personal and home care products for its powerful antimicrobial effect. Several studies have shown triclosan toxicity and the American Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2016 has limited its use. It has been recently included in endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), a list of chemicals known for their ability to interfere with hormonal signaling with particular critical effects on reproduction both in animals and humans. In order to deepen the knowledge in this specific field, the present study was undertaken to explore the effect of different concentrations of triclosan (1, 10, and 50 µM) on cultured luteal cells, isolated from swine ovaries, evaluating effects on growth Bromodeoxyuridine (BrDU) incorporation and Adenosine TriPhosphate (ATP) production, steroidogenesis (progesterone secretion) and redox status (superoxide and nitric oxide production, enzymatic and non-enzymatic scavenging activity). A biphasic effect was exerted by triclosan on P4 production. In fact, the highest concentration inhibited, while the others stimulated P4 production (p < 0.05). Triclosan significantly inhibited cell proliferation, metabolic activity, and enzymatic scavenger activity (p < 0.05). On the contrary, nitric oxide production was significantly increased by triclosan (p < 0.01), while superoxide anion generation and non-enzymatic scavenging activity were unaffected.
Keywords: corpus luteum; nitric oxide; progesterone; redox status; superoxide anion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wu J.L., Leung K.F., Sui-Fan T., Ching-Wan L. Organochlorine isotopic pattern-enhanced detection and quantification of triclosan and its metabolites in human serum by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012;26:123–132. doi: 10.1002/rcm.5303. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

