Plant-Derivatives Small Molecules with Antibacterial Activity
- PMID: 33668943
- PMCID: PMC7996626
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10030231
Plant-Derivatives Small Molecules with Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
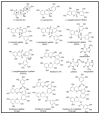
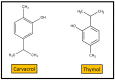
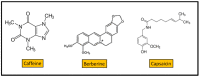
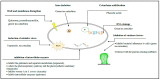
The vegetal world constitutes the main factory of chemical products, in particular secondary metabolites like phenols, phenolic acids, terpenoids, and alkaloids. Many of these compounds are small molecules with antibacterial activity, although very few are actually in the market as antibiotics for clinical practice or as food preservers. The path from the detection of antibacterial activity in a plant extract to the practical application of the active(s) compound(s) is long, and goes through their identification, purification, in vitro and in vivo analysis of their biological and pharmacological properties, and validation in clinical trials. This review presents an update of the main contributions published on the subject, focusing on the compounds that showed activity against multidrug-resistant relevant bacterial human pathogens, paying attention to their mechanisms of action and synergism with classical antibiotics.
Keywords: antibacterial activity; multi-drug resistance; plant-derivates; small molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
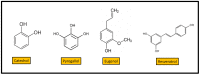
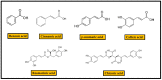
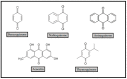
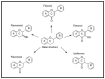
References
-
- Kessler A., Kalske A. Plant secondary metabolite diversity and species interactions. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018;49:115–138. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110617-062406. - DOI
-
- Geissman T.A. Flavonoid compounds, tannins, lignins, and related compounds. In: Florkin M., Stotz E.H., editors. Pyrrole Pigments, Isoprenoid Compounds and Phenolic Plant Constituents. Volume 9. Elsevier; New York, NY, USA: 1963. p. 265.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

