A Study Validating the Estimation of Anterior Chamber Depth and Iridocorneal Angle with Portable and Non-Portable Slit-Lamp Microscopy
- PMID: 33669487
- PMCID: PMC7921911
- DOI: 10.3390/s21041436
A Study Validating the Estimation of Anterior Chamber Depth and Iridocorneal Angle with Portable and Non-Portable Slit-Lamp Microscopy
Abstract
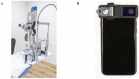
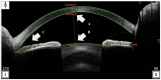
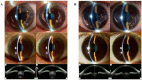
This study assessed the anterior chamber depth (ACD) and iridocorneal angle using a portable smart eye camera (SEC) compared to the conventional slit-lamp microscope and anterior-segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT). This retrospective case-control study included 170 eyes from 85 Japanese patients. The correlation between the ACD evaluations conducted with the SEC and conventional slit-lamp was high (r = 0.814). The correlation between the Van-Herick Plus grade obtained using two devices was also high (r = 0.919). A high kappa value was observed for the Van-Herick Plus grading (Kappa = 0.757). A moderate correlation was observed between the ACD measured using AS-OCT and the slit-lamp image acquired with the conventional slit-lamp microscope and SEC (r = 0.609 and 0.641). A strong correlation was observed between the trabecular-iris angle (TIA) measured using AS-OCT and Van-Herick Plus grade obtained with the conventional slit-lamp microscope and SEC (r = 0.702 and 0.764). Strong correlations of ACD evaluation and high kappa value of the Van-Herick Plus grading indicated the adequate subjective assessment function of the SEC. Moderate correlations between the ACD objective measurement and evaluation and strong correlation between the TIA and Van-Herick Plus grade suggested the good objective assessment function of the SEC. The SEC demonstrated adequate performance for ACD evaluation and angle estimation.
Keywords: anterior chamber depth; anterior-segment optical coherence tomography; slit-lamp microscope; smart eye camera; trabecular-iris angle.
Conflict of interest statement
H.Y. and E.S. are the co-founders of OUI Inc. OUI Inc. has the patent for the Smart Eye Camera (Patent No. JP; 6627071, USA; 16/964822, EU; 19743494.7, China; 201980010174.7, India; 202017033428, VN; 1-2020-04893, and Africa; AP/P2020/012569). There are no other relevant declarations relating to this patent. The other authors declare no competing interest associated with this manuscript. OUI Inc. did not have any role in the funding, study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Blomquist P.H. Practical Ophthalmology: A Manual for Beginning Residents. 7th ed. American Academy of Ophthalmology; San Francisco, CA, USA: 2015.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

