Functions of ROS in Macrophages and Antimicrobial Immunity
- PMID: 33669824
- PMCID: PMC7923022
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10020313
Functions of ROS in Macrophages and Antimicrobial Immunity
Abstract
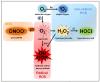
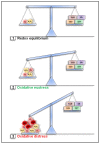
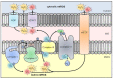
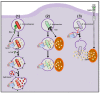
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are a chemically defined group of reactive molecules derived from molecular oxygen. ROS are involved in a plethora of processes in cells in all domains of life, ranging from bacteria, plants and animals, including humans. The importance of ROS for macrophage-mediated immunity is unquestioned. Their functions comprise direct antimicrobial activity against bacteria and parasites as well as redox-regulation of immune signaling and induction of inflammasome activation. However, only a few studies have performed in-depth ROS analyses and even fewer have identified the precise redox-regulated target molecules. In this review, we will give a brief introduction to ROS and their sources in macrophages, summarize the versatile roles of ROS in direct and indirect antimicrobial immune defense, and provide an overview of commonly used ROS probes, scavengers and inhibitors.
Keywords: NADPH oxidases; ROS detection; ROS scavenging; antimicrobial defense; immunity; infection; inflammasome; macrophages; mitochondria; reactive oxygen species; redox signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

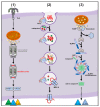
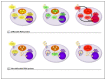
References
-
- Fenton H.J.H. LXXIII.—Oxidation of tartaric acid in presence of iron. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1894;65:899–910. doi: 10.1039/CT8946500899. - DOI
-
- Haber F., Weiss J., Pope W.J. The catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by iron salts. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1997;147:332–351.
-
- Prousek J. Fenton chemistry in biology and medicine. Pure Appl. Chem. 2007;79:2325–2338. doi: 10.1351/pac200779122325. - DOI
-
- Das K., Roychoudhury A. Reactive oxygen species (ros) and response of antioxidants as ros-scavengers during environmental stress in plants. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014;2:53. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2014.00053. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

