The Effect of a Polyester Nanofibrous Membrane with a Fibrin-Platelet Lysate Coating on Keratinocytes and Endothelial Cells in a Co-Culture System
- PMID: 33670150
- PMCID: PMC7916860
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11020457
The Effect of a Polyester Nanofibrous Membrane with a Fibrin-Platelet Lysate Coating on Keratinocytes and Endothelial Cells in a Co-Culture System
Abstract
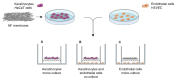
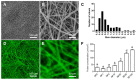
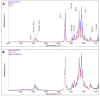
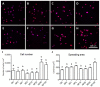
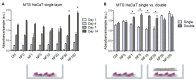
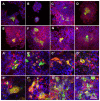
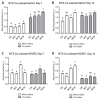
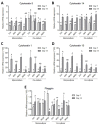
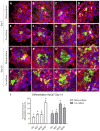
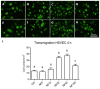
Chronic wounds affect millions of patients worldwide, and it is estimated that this number will increase steadily in the future due to population ageing. The research of new therapeutic approaches to wound healing includes the development of nanofibrous meshes and the use of platelet lysate (PL) to stimulate skin regeneration. This study considers a combination of a degradable electrospun nanofibrous blend of poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) and poly(ε-caprolactone) (PLCL/PCL) membranes (NF) and fibrin loaded with various concentrations of PL aimed at the development of bioactive skin wound healing dressings. The cytocompatibility of the NF membranes, as well as the effect of PL, was evaluated in both monocultures and co-cultures of human keratinocytes and human endothelial cells. We determined that the keratinocytes were able to adhere on all the membranes, and their increased proliferation and differentiation was observed on the membranes that contained fibrin with at least 50% of PL (Fbg + PL) after 14 days. With respect to the co-culture experiments, the membranes with fibrin with 20% of PL were observed to enhance the metabolic activity of endothelial cells and their migration, and the proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes. The results suggest that the newly developed NF combined with fibrin and PL, described in the study, provides a promising dressing for chronic wound healing purposes.
Keywords: electrospun nanofibre; endothelial cells; fibrin; in vitro co-culture system; keratinocytes; platelet lysate; skin wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sen C.K., Gordillo G.M., Roy S., Kirsner R., Lambert L., Hunt T.K., Gottrup F., Gurtner G.C., Longaker M.T. Human skin wounds: A major and snowballing threat to public health and the economy: PERSPECTIVE ARTICLE. Wound Repair Regen. 2009;17:763–771. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-475X.2009.00543.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bacakova L., Zikmundova M., Pajorova J., Broz A., Filova E., Blanquer A., Matejka R., Stepanovska J., Mikes P., Jencova V., et al. Applications of Nanobiotechnology. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2020. Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Skin Tissue Engineering and Wound Healing Based on Synthetic Polymers.
-
- Losi P., Barsotti M.C., Foffa I., Buscemi M., De Almeida C.V., Fabbri M., Gabbriellini S., Nocchi F., Ursino S., Urciuoli P., et al. In vitro human cord blood platelet lysate characterisation with potential application in wound healing. Int. Wound J. 2020;17:65–72. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13233. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- NV18-01-00332/Czech Health Research Council, Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic
- LM2018129 Czech-BioImaging/Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic
- National Sustainability Programme II, project BIOCEV-FAR LQ1604/Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

