Pentacyclic Triterpene Profile and Its Biosynthetic Pathway in Cecropia telenitida as a Prospective Dietary Supplement
- PMID: 33670502
- PMCID: PMC7922737
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26041064
Pentacyclic Triterpene Profile and Its Biosynthetic Pathway in Cecropia telenitida as a Prospective Dietary Supplement
Abstract
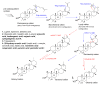
Promising research over the past decades has shown that some types of pentacyclic triterpenes (PTs) are associated with the prevention of type 2 diabetes (T2D), especially those found in foods. The most abundant edible sources of PTs are those belonging to the ursane and oleanane scaffold. The principal finding is that Cecropia telenitida contains abundant oleanane and ursane PT types with similar oxygenation patterns to those found in food matrices. We studied the compositional profile of a rich PT fraction (DE16-R) and carried out a viability test over different cell lines. The biosynthetic pathway connected to the isolated PTs in C. telenitida offers a specific medicinal benefit related to the modulation of T2D. This current study suggests that this plant can assemble isobaric, positional isomers or epimeric PT. Ursane or oleanane scaffolds with the same oxygenation pattern are always shared by the PTs in C. telenitida, as demonstrated by its biosynthetic pathway. Local communities have long used this plant in traditional medicine, and humans have consumed ursane and oleanane PTs in fruits since ancient times, two key points we believe useful in considering the medicinal benefits of C. telenitida and explaining how a group of molecules sharing a closely related scaffold can express effectiveness.
Keywords: Cecropia telenitida; dietary supplement; pentacyclic triterpene; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
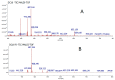

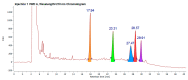
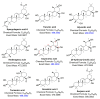
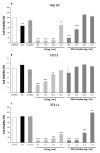
References
-
- De la Torre R., Carbó M., Pujadas M., Biel S., Mesa M.D., Covas M.I., Expósito M., Espejo J.A., Sanchez-Rodriguez E., Díaz-Pellicer P., et al. Pharmacokinetics of maslinic and oleanolic acids from olive oil—Effects on endothelial function in healthy adults. A randomized, controlled, dose–response study. Food Chem. 2020;322:126676. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126676. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wu J.B., Kuo Y.H., Lin C.H., Ho H.Y., Shih C.C. Tormentic Acid, a major component of suspension cells of eriobotrya japonica, suppresses high-fat diet-induced diabetes and hyperlipidemia by glucose transporter 4 and amp-activated protein kinase phosphorylation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014;62:10717–10726. doi: 10.1021/jf503334d. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

