Nitric Oxide Enhances Photosynthetic Nitrogen and Sulfur-Use Efficiency and Activity of Ascorbate-Glutathione Cycle to Reduce High Temperature Stress-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plants
- PMID: 33670537
- PMCID: PMC7922496
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11020305
Nitric Oxide Enhances Photosynthetic Nitrogen and Sulfur-Use Efficiency and Activity of Ascorbate-Glutathione Cycle to Reduce High Temperature Stress-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plants
Abstract
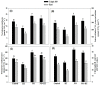
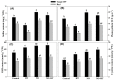
The effects of nitric oxide (NO) as 100 µM sodium nitroprusside (SNP, NO donor) on photosynthetic-nitrogen use efficiency (NUE), photosynthetic-sulfur use efficiency (SUE), photosynthesis, growth and agronomic traits of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars, Taipie-309 (high photosynthetic-N and SUE) and Rasi (low photosynthetic-N and SUE) were investigated under high temperature stress (40 °C for 6 h). Plants exposed to high temperature stress caused significant reduction in photosynthetic activity, use efficiency of N and S, and increment in H2O2 and thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) content. The drastic effects of high temperature stress were more pronounced in cultivar Rasi than Taipie-309. However, foliar spray of SNP decreased the high temperature induced H2O2 and TBARS content and increased accumulation of proline and activity of ascorbate-glutathione cycle that collectively improved tolerance to high temperature stress more effectively in Taipie-309. Exogenously applied SNP alleviated the high temperature induced decrease in photosynthesis through maintaining higher photosynthetic-NUE and photosynthetic-SUE, activity of ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco), and synthesis of reduced glutathione (GSH). The use of 2-4-carboxyphenyl-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxy-3-oxide (cPTIO, NO scavenger) substantiated the study that in the absence of NO oxidative stress increased, while NO increased photosynthetic-NUE and photosynthetic-SUE, net photosynthesis and plant dry mass. Taken together, the present investigation reveals that NO increased heat stress tolerance and minimized high temperature stress adversaries more effectively in cultivar Taipie-309 than Rasi by enhancing photosynthetic-NUE and SUE and strengthening the antioxidant defense system.
Keywords: Oryza sativa; antioxidants; reactive oxygen species; sodium nitroprusside; stomata.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) Crops/Regions/World List/Production Quantity (Pick Lists), Rice (Paddy) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); Rome, Italy: 2014.
-
- FAOSTAT, Faostat.fao.org. [(accessed on 10 October 2020)];2011 Available online: http://www.fao.org/india/fao-in-india/india-at-a-glance/en/
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) Statistics of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO); Rome, Italy: 2015.
-
- Shahbandeh M. Total Rice Consumption Worldwide from 2008/2009 to 2018/2019. [(accessed on 10 October 2020)];2019 Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/255977/total-global-rice-consumption/
-
- IPCC . The Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty. IPCC; Geneva, Switzerland: 2018. Global Warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C Above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

