Attempt to Develop Rat Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Model Using Yamakagashi (Rhabdophis tigrinus) Venom Injection
- PMID: 33670557
- PMCID: PMC7922536
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins13020160
Attempt to Develop Rat Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Model Using Yamakagashi (Rhabdophis tigrinus) Venom Injection
Abstract
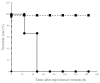
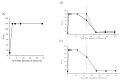
Disseminated intravascular coagulation, a severe clinical condition caused by an underlying disease, involves a markedly continuous and widespread activation of coagulation in the circulating blood and the formation of numerous microvascular thrombi. A snakebite, including that of the Yamakagashi (Rhabdophis tigrinus), demonstrates this clinical condition. Thus, an animal model using Yamakagashi venom was constructed. Yamakagashi venom was administered to rats, and its lethality and the changes in blood coagulation factors were detected after venom injection. When 300 μg venom was intramuscularly administered to 12-week-old rats, (1) they exhibited hematuria with plasma hemolysis and died within 48 h; (2) Thrombocytopenia in the blood was observed in the rats; (3) irreversible prolongation of prothrombin time in the plasma to the measurement limit occurred; (4) fibrinogen concentration in the plasma irreversibly decreased below the measurement limit; and (5) A transient increase in the plasma concentration of D-dimer was observed. In this model, a fixed amount of Rhabdophis tigrinus venom injection resulted in the clinical symptom similar to the human pathology with snakebite. The use of the rat model is very effective in validating the therapeutic effect of human disseminated intravascular coagulation condition due to snakebite.
Keywords: D-dimer; Yamakagashi (Rhabdophis tigrinus) venom; anti-Yamakagashi equine antibody; lethality; rat disseminated intravascular coagulation model; thrombocytopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Attempt for a Recombinant Thrombomodulin Alpha Treatment in a Rat Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Model Using Yamakagashi (Rhabdophis tigrinus) Venom.Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 2;14(5):322. doi: 10.3390/toxins14050322. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35622569 Free PMC article.
-
Early pathology in venom-induced consumption coagulopathy by Rhabdophis tigrinus (Yamakagashi snake) envenomation.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2019 Jul;57(7):668-671. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2018.1540045. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2019. PMID: 30689439
-
Comparative Study of Biological Activities of Venom from Colubrid Snakes Rhabdophis tigrinus (Yamakagashi) and Rhabdophis lateralis.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Nov 17;9(11):373. doi: 10.3390/toxins9110373. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29149042 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical feature of envenomation by the snake, Yamakagashi (Rhabdophis tigrinus)].Chudoku Kenkyu. 2007 Jul;20(3):235-43. Chudoku Kenkyu. 2007. PMID: 17784557 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Action of snake venom components on the haemostatic system.Blood Rev. 1993 Sep;7(3):176-89. doi: 10.1016/0268-960x(93)90004-n. Blood Rev. 1993. PMID: 8241832 Review.
Cited by
-
Rhabdophis tigrinus (Yamakagashi) Bites in Japan Over the Last 50 Years: A Retrospective Survey.Front Public Health. 2022 Jan 10;9:775458. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.775458. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35083190 Free PMC article.
-
Attempt for a Recombinant Thrombomodulin Alpha Treatment in a Rat Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Model Using Yamakagashi (Rhabdophis tigrinus) Venom.Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 2;14(5):322. doi: 10.3390/toxins14050322. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35622569 Free PMC article.
-
Rodent Lethality Models Are Problematic for Evaluating Antivenoms for Human Envenoming.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 3;13:830384. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.830384. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35185582 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jourdain M., Tournoys A., Leroy X., Mangalaboyi J., Fourrier F., Goudemand J., Gosselin B., Vallet B., Chopin C. Effect of N omega-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester on the endovenom-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation in porcine sep-tic shock. Crit. Care. Med. 1997;25:452–459. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199703000-00014. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

