Knockdown of AKT3 Activates HER2 and DDR Kinases in Bone-Seeking Breast Cancer Cells, Promotes Metastasis In Vivo and Attenuates the TGFβ/CTGF Axis
- PMID: 33670586
- PMCID: PMC7922044
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10020430
Knockdown of AKT3 Activates HER2 and DDR Kinases in Bone-Seeking Breast Cancer Cells, Promotes Metastasis In Vivo and Attenuates the TGFβ/CTGF Axis
Abstract
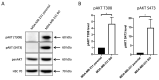
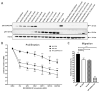
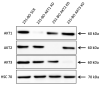
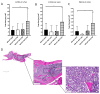
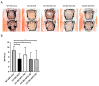
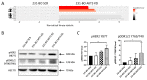
Bone metastases frequently occur in breast cancer patients and lack appropriate treatment options. Hence, understanding the molecular mechanisms involved in the multistep process of breast cancer bone metastasis and tumor-induced osteolysis is of paramount interest. The serine/threonine kinase AKT plays a crucial role in breast cancer bone metastasis but the effect of individual AKT isoforms remains unclear. Therefore, AKT isoform-specific knockdowns were generated on the bone-seeking MDA-MB-231 BO subline and the effect on proliferation, migration, invasion, and chemotaxis was analyzed by live-cell imaging. Kinome profiling and Western blot analysis of the TGFβ/CTGF axis were conducted and metastasis was evaluated by intracardiac inoculation of tumor cells into NOD scid gamma (NSG) mice. MDA-MB-231 BO cells exhibited an elevated AKT3 kinase activity in vitro and responded to combined treatment with AKT- and mTOR-inhibitors. Knockdown of AKT3 significantly increased migration, invasion, and chemotaxis in vitro and metastasis to bone but did not significantly enhance osteolysis. Furthermore, knockdown of AKT3 increased the activity and phosphorylation of pro-metastatic HER2 and DDR1/2 but lowered protein levels of CTGF after TGFβ-stimulation, an axis involved in tumor-induced osteolysis. We demonstrated that AKT3 plays a crucial role in bone-seeking breast cancer cells by promoting metastatic potential without facilitating tumor-induced osteolysis.
Keywords: AKT; AKT isoforms; bone metastasis; breast cancer; metastasis; organ tropism; osteolysis; vicious cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Downregulation of AKT3 Increases Migration and Metastasis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Upregulating S100A4.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 7;11(1):e0146370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146370. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26741489 Free PMC article.
-
Asperolide A prevents bone metastatic breast cancer via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/c-Fos/NFATc1 signaling pathway.Cancer Med. 2020 Nov;9(21):8173-8185. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3432. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32976685 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic role of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) in osteolytic metastasis of breast cancer.J Bone Miner Res. 2006 Jul;21(7):1045-59. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.060416. J Bone Miner Res. 2006. PMID: 16813525
-
Parathyroid hormone-related protein and bone metastases.Cancer. 1997 Oct 15;80(8 Suppl):1572-80. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0142(19971015)80:8+<1572::aid-cncr7>3.3.co;2-d. Cancer. 1997. PMID: 9362424 Review.
-
When tumor suppressor TGFβ meets the HER2 (ERBB2) oncogene.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2011 Jun;16(2):81-8. doi: 10.1007/s10911-011-9206-4. Epub 2011 Apr 6. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 21590373 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AKT in Bone Metastasis of Solid Tumors: A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 11;13(10):2287. doi: 10.3390/cancers13102287. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34064589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipopolysaccharide promotes cancer cell migration and invasion through METTL3/PI3K/AKT signaling in human cholangiocarcinoma.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 16;10(8):e29683. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29683. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38681552 Free PMC article.
-
Akt isoforms differentially provide for chemoresistance in prostate cancer.Cancer Biol Med. 2021 Oct 1;19(5):635-50. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0747. Cancer Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34591413 Free PMC article.
-
Hypomethylation-driven AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 3 promotes testicular germ cell tumors proliferation and negatively correlates to immune infiltration.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):11288-11302. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2002621. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34882061 Free PMC article.
-
SHIP1 Is Present but Strongly Downregulated in T-ALL, and after Restoration Suppresses Leukemia Growth in a T-ALL Xenotransplantation Mouse Model.Cells. 2023 Jul 6;12(13):1798. doi: 10.3390/cells12131798. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hiraga T., Williams P.J., Mundy G.R., Yoneda T. The bisphosphonate ibandronate promotes apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells in bone metastases. Cancer Res. 2001;61:4418–4424. - PubMed
-
- Goldhirsch A., Wood W.C., Coates A.S., Gelber R.D., Thurlimann B., Senn H.J., Panel m. Strategies for subtypes--dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011;22:1736–1747. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr304. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

