Optimized Identification of High-Grade Prostate Cancer by Combining Different PSA Molecular Forms and PSA Density in a Deep Learning Model
- PMID: 33670632
- PMCID: PMC7922417
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11020335
Optimized Identification of High-Grade Prostate Cancer by Combining Different PSA Molecular Forms and PSA Density in a Deep Learning Model
Abstract
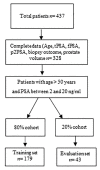
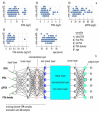
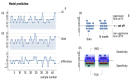
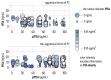
After skin cancer, prostate cancer (PC) is the most common cancer among men. The gold standard for PC diagnosis is based on the PSA (prostate-specific antigen) test. Based on this preliminary screening, the physician decides whether to proceed with further tests, typically prostate biopsy, to confirm cancer and evaluate its aggressiveness. Nevertheless, the specificity of the PSA test is suboptimal and, as a result, about 75% of men who undergo a prostate biopsy do not have cancer even if they have elevated PSA levels. Overdiagnosis leads to unnecessary overtreatment of prostate cancer with undesirable side effects, such as incontinence, erectile dysfunction, infections, and pain. Here, we used artificial neuronal networks to develop models that can diagnose PC efficiently. The model receives as an input a panel of 4 clinical variables (total PSA, free PSA, p2PSA, and PSA density) plus age. The output of the model is an estimate of the Gleason score of the patient. After training on a dataset of 190 samples and optimization of the variables, the model achieved values of sensitivity as high as 86% and 89% specificity. The efficiency of the method can be improved even further by training the model on larger datasets.
Keywords: PSA density; PSA molecular forms; artificial neural network; prostate cancer; tumor markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Combinatorial Neural Network Analysis Reveals a Synergistic Behaviour of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance and Prostate Health Index in the Identification of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2022 Oct;20(5):e406-e410. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2022.04.013. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35610113
-
Prostate cancer screening in men aged 50 to 69 years (STHLM3): A prospective population-based diagnostic study. Grönberg H, Adolfsson J, Aly M, Nordström T, Wiklund P, Brandberg Y, Thompson J, Wiklund F, Lindberg J, Clements M, Egevad L, Eklund M.Lancet Oncol. 2015 Dec;16(16):1667-76. [Epub 2015 Nov 10]. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00361-7.Urol Oncol. 2017 Mar;35(3):120. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.03.013. Urol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28215847
-
An artificial neural network for prostate cancer staging when serum prostate specific antigen is 10 ng./ml. or less.J Urol. 2003 May;169(5):1724-8. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000062548.28015.f6. J Urol. 2003. PMID: 12686818
-
Clinical performance of serum [-2]proPSA derivatives, %p2PSA and PHI, in the detection and management of prostate cancer.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2014 Dec 25;2(4):343-50. eCollection 2014. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2014. PMID: 25606581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostatic specific antigen and bone scan in the diagnosis and follow-up of prostate cancer. Can diagnostic significance of PSA be increased?Hell J Nucl Med. 2012 Sep-Dec;15(3):241-6. Hell J Nucl Med. 2012. PMID: 23227460 Review.
Cited by
-
Combining Magnetic Resonance Diffusion-Weighted Imaging with Prostate-Specific Antigen to Differentiate Between Malignant and Benign Prostate Lesions.Med Sci Monit. 2022 Apr 23;28:e935307. doi: 10.12659/MSM.935307. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 35459760 Free PMC article.
-
A Neural Network Model Combining [-2]proPSA, freePSA, Total PSA, Cathepsin D, and Thrombospondin-1 Showed Increased Accuracy in the Identification of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 21;15(5):1355. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051355. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900150 Free PMC article.
-
Reply to Jue et al. Value of MRI to Improve Deep Learning Model That Identifies High-Grade Prostate Cancer. Comment on "Gentile et al. Optimized Identification of High-Grade Prostate Cancer by Combining Different PSA Molecular Forms and PSA Density in a Deep Learning Model. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 335".Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jul 6;11(7):1214. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11071214. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359297 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios alone or combined with prostate-specific antigen for the diagnosis of prostate cancer and clinically significant prostate cancer.Asian J Urol. 2023 Apr;10(2):158-165. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2022.02.007. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Asian J Urol. 2023. PMID: 36942115 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Deep Learning in Prostate Cancer Management: Past, Present and Future Based on a Comprehensive Literature Review.J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 21;11(13):3575. doi: 10.3390/jcm11133575. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35806859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mottet N., van den Bergh R.C.N., Briers E., Van den Broeck T., Cumberbatch M.G., De Santis M., Fanti S., Fossati N., Gandaglia G., Gillessen S., et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2020 Update. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.09.042. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

