Refining Knowledge of Factors Affecting Vitamin B12 Concentration in Bovine Milk
- PMID: 33670816
- PMCID: PMC7922057
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11020532
Refining Knowledge of Factors Affecting Vitamin B12 Concentration in Bovine Milk
Abstract
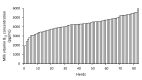
Milk is an excellent source of vitamin B12 (B12) for humans. Therefore, being able to guarantee a high and consistent concentration of this vitamin would enhance consumer perception of milk as a health food. The aim of the paper was to gather additional knowledge on factors that could explain B12 variation in cow milk through two observational studies: (1) to explore the relationship between milk B12 and ruminal conditions, such as pH and volatile fatty acid concentrations; and (2) to examine the impact of bedding on B12 concentrations in bulk tank milk. For study 1, a total of 72 milk and ruminal liquid samples were obtained from 45 Holstein cows fitted with ruminal cannula between 10 and 392 days of lactation. For study 2, bulk tank milk samples were obtained from 83 commercial herds; 26 herds used recycled manure solid bedding and 57 used straw bedding. Milk samples were analyzed for B12 using radioassay. Using principal component regression analysis, we observed that ruminal pH and the acetate:propionate ratio for cows receiving the early lactation ration were positively correlated with milk B12. Bedding did not influence milk B12 in bulk tanks, which averaged 4276 pg/mL. In conclusion, as B12 is synthesized by ruminal bacteria, optimizing ruminal conditions had a positive effect on milk B12, while bedding management had no influence.
Keywords: bovine milk; cattle; cyanocobalamin; environmental factor; milk quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Crane F.G., Clarke T.K. Attitudes towards milk: A canadian view. Br. Food J. 1989;91:6–9. doi: 10.1108/EUM0000000002313. - DOI
-
- Smith L.M. Trends in per capita consumption of dairy foods. J. Dairy Sci. 1982;65:469–475. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(82)82217-0. - DOI
-
- Canadian Dairy Information Centre Global Consumption of Dairy Products-Total Fluid Milk Consumption for Selected Countries. [(accessed on 9 April 2020)]; Available online: https://aimis-simia-cdic-ccil.agr.gc.ca/rp/index-eng.cfm?action=gR&r=264....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources