Triborheological Study under Physiological Conditions of PVA Hydrogel/HA Lubricant as Synthetic System for Soft Tissue Replacement
- PMID: 33670837
- PMCID: PMC7957559
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13050746
Triborheological Study under Physiological Conditions of PVA Hydrogel/HA Lubricant as Synthetic System for Soft Tissue Replacement
Abstract
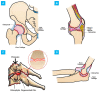
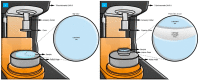
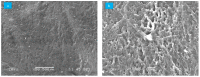
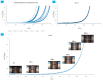
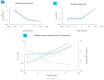
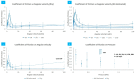
In soft tissue replacement, hydrophilic, flexible, and biocompatible materials are used to reduce wear and coefficient of friction. This study aims to develop and evaluate a solid/liquid triborheological system, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/hyaluronic acid (HA), to mimic conditions in human synovial joints. Hydrogel specimens prepared via the freeze-thawing technique from a 10% (w/v) PVA aqueous solution were cut into disc shapes (5 ± 0.5 mm thickness). Compression tests of PVA hydrogels presented a Young's modulus of 2.26 ± 0.52 MPa. Friction tests were performed on a Discovery Hybrid Rheometer DHR-3 under physiological conditions using 4 mg/mL HA solution as lubricant at 37 °C. Contact force was applied between 1 and 20 N, highlighting a coefficient of friction change of 0.11 to 0.31 between lubricated and dry states at 3 N load (angular velocity: 40 rad/s). Thermal behavior was evaluated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) in the range of 25-250 °C (5 °C/min rate), showing an endothermic behavior with a melting temperature (Tm) around 231.15 °C. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) tests showed a microporous network that enhanced water content absorption to 82.99 ± 1.5%. Hydrogel achieved solid/liquid lubrication, exhibiting a trapped lubricant pool that supported loads, keeping low coefficient of friction during lubricated tests. In dry tests, interstitial water evaporates continuously without countering sliding movement friction.
Keywords: coefficient of friction; hyaluronic acid lubricant; polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel; triborheology; wear.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Experimental and numerical tribological studies of a boundary lubricant functionalized poro-viscoelastic PVA hydrogel in normal contact and sliding.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012 Oct;14:248-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.06.009. Epub 2012 Jun 27. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012. PMID: 22947923
-
Friction and wear behavior of poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) hydrogels for articular cartilage replacement.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007 Nov;83(2):471-9. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.31238. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007. PMID: 17492689
-
Preparation, optimization and property of PVA-HA/PAA composite hydrogel.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017 Sep 1;78:520-529. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.04.117. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017. PMID: 28576017
-
Preparation and property of high strength and low friction PVA-HA/PAA composite hydrogel using annealing treatment.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018 Oct 1;91:579-588. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.05.080. Epub 2018 May 30. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018. PMID: 30033290
-
Biphasic and boundary lubrication mechanisms in artificial hydrogel cartilage: A review.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2015 Dec;229(12):864-78. doi: 10.1177/0954411915611160. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2015. PMID: 26614800 Review.
Cited by
-
Aqueous lubrication and wear properties of nonionic bottle-brush polymers.RSC Adv. 2022 Jun 15;12(28):17740-17746. doi: 10.1039/d2ra02711a. eCollection 2022 Jun 14. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35765345 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembly of gelatin and collagen in the polyvinyl alcohol substrate and its influence on cell adhesion, proliferation, shape, spreading and differentiation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jul 14;11:1193849. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1193849. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37520293 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Polymeric Scaffolds for Stem Cell Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Sep 22;16(18):2667. doi: 10.3390/polym16182667. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339131 Free PMC article.
-
Triborheological Analysis of Reconstituted Gastrointestinal Mucus/Chitosan:TPP Nanoparticles System to Study Mucoadhesion Phenomenon under Different pH Conditions.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;14(22):4978. doi: 10.3390/polym14224978. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36433107 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress in Hydrogel-Based Synthetic Cartilage: Focus on Lubrication and Load-Bearing Capacities.Gels. 2023 Feb 8;9(2):144. doi: 10.3390/gels9020144. Gels. 2023. PMID: 36826314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- OMS Prevención de Trastornos Musculoesqueléticos en el Lugar de Trabajo: Serie Protección de la Salud de los Trabajadores n 5; 2004. [(accessed on 1 February 2021)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/occupational_health/publications/muscdisorders/es/
-
- Mahir L., Belhaj K., Zahi S., Zanmasso H., Lmidmani F., el Fatimi A. Impact of knee osteoarthritis on the quality of life. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2016;59:155–159. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2016.07.345. - DOI
-
- Kumar H.N.H., Nagaraj K., Luthra K., Gupta P., Sapar P., Gupta S., Tyagi A. Health-related quality of life among osteoarthritis patients attending primary care clinics of mangalore city. Int. J. Med. Public Health. 2015;5:55–58. doi: 10.4103/2230-8598.151260. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

