Exopolysaccharide from Porphyridium cruentum (purpureum) is Not Toxic and Stimulates Immune Response against Vibriosis: The Assessment Using Zebrafish and White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei
- PMID: 33670856
- PMCID: PMC7997376
- DOI: 10.3390/md19030133
Exopolysaccharide from Porphyridium cruentum (purpureum) is Not Toxic and Stimulates Immune Response against Vibriosis: The Assessment Using Zebrafish and White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei
Abstract
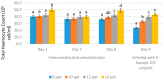
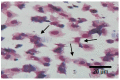
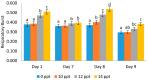
Exopolysaccharides, or extracellular polysaccharides (EPS, sPS), represent a valuable metabolite compound synthesized from red microalgae. It is a non-toxic natural agent and can be applied as an immunostimulant. The toxicity test of exopolysaccharides from Porphyridium has been done in vivo using zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryonic model, or the ZET (zebrafish embryotoxicity test). The administration of extracellular polysaccharides or exopolysaccharides (EPS) from microalgae Porphyridium cruentum (synonym: P. purpureum) to shrimps Litopenaeus vannamei was investigated to determine the effect of this immunostimulant on their non-specific immune response and to test if this compound can be used as a protective agent for shrimps in relation to Vibrio infection. For immune response, exopolysaccharides were given to shrimps via the immersion method on day 1 and booster on day 8. Shrimp hemocytes were taken on day 1 (EPS administration), day 7 (no treatment), day 8 (EPS booster) and day 9 (Vibrio infection) and tested for their immune response on each treatment. The result shows that the EPS is not toxic, as represented by the normal embryonic development and the mortality data. In the Pacific white shrimps, an increase in the values of all immune parameters was shown, in line with the increasing EPS concentration, except for the differential hemocyte count (DHC). In detail, an increase was noted in total hemocytes (THC) value, phagocytotic activity (PA) and respiratory burst (RB) in line with the EPS concentration increase. These results and other previous studies indicate that EPS from Porphyridium is safe, enhances immune parameters in shrimp rapidly, and has the ability to act as an immunostimulant or an immunomodulator. It is a good modulator for the non-specific immune cells of Pacific white shrimps, and it can be used as a preventive agent against vibriosis.
Keywords: Danio rerio; Vibrio harveyi; extracellular polysaccharide; hemocytes; immunomodulator; innate immune cells; microalgae; phagocytic activity; respiratory burst; toxicity; white shrimp.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The known two types of transglutaminases regulate immune and stress responses in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei.Dev Comp Immunol. 2016 Jun;59:164-76. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2016.02.003. Epub 2016 Feb 6. Dev Comp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26855013
-
Noradrenaline modulates the immunity of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006 Jul;21(1):11-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2005.09.003. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16377211
-
Studies on the immunomodulatory effect of polysaccharide gel extracted from Durio zibethinus in Penaeus monodon shrimp against Vibrio harveyi and WSSV.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010 Apr;28(4):555-61. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2009.12.009. Epub 2009 Dec 23. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20034573
-
The immune response of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and its susceptibility to Vibrio infection in relation with the moult cycle.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004 Feb;16(2):151-61. doi: 10.1016/S1050-4648(03)00058-5. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15123319
-
Anti-vibrio and immune-enhancing activity of medicinal plants in shrimp: A comprehensive review.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021 Oct;117:192-210. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2021.08.006. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34400334 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Production and Fluorescence Characteristics of Phycoerythrin from Three Strains of Porphyridium.Foods. 2022 Jul 12;11(14):2069. doi: 10.3390/foods11142069. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35885311 Free PMC article.
-
Microalgae-Based Biorefineries: Challenges and Future Trends to Produce Carbohydrate Enriched Biomass, High-Added Value Products and Bioactive Compounds.Biology (Basel). 2022 Jul 29;11(8):1146. doi: 10.3390/biology11081146. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Immunostimulants in Shrimp Farming-A Bioeconomic Perspective.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jan 7;15(2):124. doi: 10.3390/ani15020124. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of Bioactive Peptides from Porphyridium sp. and Assessment of Their Potential for Use in the Prevention of Hypertension, Inflammation and Pain.Mar Drugs. 2023 Jul 25;21(8):422. doi: 10.3390/md21080422. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37623703 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral activity of red algae phycocolloids against herpes simplex virus type 2 in vitro.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2023 Apr 23;38:e00798. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2023.e00798. eCollection 2023 Jun. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2023. PMID: 37181274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WWF-Indonesia . Budidaya Udang Vannamei, Tambak Semi Intensif Dengan Instalasi Pengolahan Air Limbah (IPAL) WWF-Indonesia; Jakarta, Indonesia: 2014. p. 38. Better Management Practices.
-
- Martinez F.S. Boletines Nicovita. SAA Technical; Johannesburg, South Africa: 2007. The Immune System of Shrimp; pp. 1–6. Nicovita-ALICORP SAA Technical Service.
-
- Widanarni, Meha D., Nuryati S., Sukendadan, Suwanto A. Uji Patogenisitas Vibrio harveyi pada Larva Udang Windu Menggunakan Resistensi Rifampisin Sebagai Penanda Molekuler. J. Akuakultur Indones. 2004;3:23–27. doi: 10.19027/jai.3.23-27. - DOI
-
- Supriyadi H., Rukyani A. The Use of Chemotherapuetic Agents for the Treatment of Bacterial Disease of Fish and Shrimp in Indonesia. Asian Fisheries Society; Manila, Philippines: 1992. pp. 515–517.
-
- Widowati I., Zainuri M., Kusumaningrum H.P., Maesaroh Y., Hardivillier Y., Leignel V., Bourgougnon N., Mouget J.L. Identification of agents causing vibriosis in Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp culture in Kendal, Central Java, Indonesia and application of microalgae Dunaliella salina and Tetraselmis chui as bio-control agents against vibriosis. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2018;11:101–107.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

