6-Gingerol, a Bioactive Compound of Ginger Attenuates Renal Damage in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats by Regulating the Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
- PMID: 33670981
- PMCID: PMC7997342
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13030317
6-Gingerol, a Bioactive Compound of Ginger Attenuates Renal Damage in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats by Regulating the Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Abstract
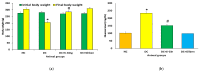
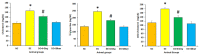
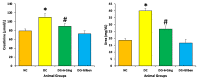
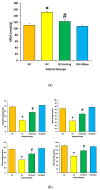
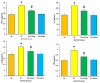
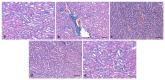
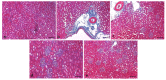
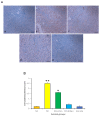
The aim of present study is to investigate the role of 6-gingerol in ameliorating the renal injury in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. The diabetes was induced by using a single dose of freshly prepared STZ (55 mg/kg body weight) intraperitoneally which causes the degeneration of pancreatic Langerhans islet β-cells. The diabetic rats were treated with oral gavage of 6-gingerol (10 mg/kg b.w.). The treatment plan was continued for 8 weeks successively and the body weight and fasting blood glucose levels were weekly checked. The biochemical parameters like lipid profile, kidney profile, antioxidant enzyme levels, lipid peroxidation and anti-inflammatory marker levels were investigated after the treatment plant. The pathological condition of kidneys was examined by haematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining besides this analysis of NF-κB protein expression by immuno-histochemistry was performed. Some of the major parameters in diabetes control vs. normal control were reported as fasting blood glucose (234 ± 10 vs. 102 ± 8 mg/dL), serum creatinine (109.7 ± 7.2 vs. 78.9 ± 4.5 μmol/L) and urea (39.9 ± 1.8 vs. 18.6 mg/dL), lipid profile levels were significantly enhanced in diabetic rats. Moreover, diabetic rats were marked with decreased antioxidant enzyme levels and increased inflammatory markers. Treatment with 6-gingerol significantly restored the fasting blood glucose level, hyperlipidaemia, Malondialdehyde (MDA) and inflammatory marker levels, NF-κB protein expression and augmented the antioxidant enzyme levels in the kidneys of diabetic rats. The kidney damage was significantly normalized by the treatment of 6-gingerol and it provides an evidence that this novel compound plays a significant role in the protection of kidney damage. These findings demonstrate that 6-gingerol reduces lipid parameters, inflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic rats, thereby inhibiting the renal damage. Our results demonstrate that use of 6-gingerol could be a novel therapeutic approach to prevent the kidney damage associated with the diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: 6-gingerol; diabetes mellitus; inflammation; oxidative stress; renal damage.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory and renal protective effect of gingerol in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats via inflammatory mechanism.Inflammopharmacology. 2019 Dec;27(6):1243-1254. doi: 10.1007/s10787-019-00569-6. Epub 2019 Mar 2. Inflammopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30826930
-
Quercetin, a Plant Flavonol Attenuates Diabetic Complications, Renal Tissue Damage, Renal Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.Metabolites. 2023 Jan 15;13(1):130. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010130. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36677055 Free PMC article.
-
The modulatory role of prime identified compounds in the bioactive fraction of Homalium zeylanicum in high-fat diet fed-streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;260:113099. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113099. Epub 2020 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32535241
-
Diltiazem attenuates oxidative stress in diabetic rats.Ren Fail. 2005;27(3):335-44. Ren Fail. 2005. PMID: 15957552
-
Gingerol, a Natural Antioxidant, Attenuates Hyperglycemia and Downstream Complications.Metabolites. 2022 Dec 16;12(12):1274. doi: 10.3390/metabo12121274. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36557312 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural compounds proposed for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024 Apr 1;14(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s13659-024-00445-z. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2024. PMID: 38556609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Zingiber officinale on Lipid Profile and Some Inflammatory Markers in Diabetic Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 May 16;2023:7154172. doi: 10.1155/2023/7154172. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37228303 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotective effect of a novel combination of 6-gingerol and metformin in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats via targeting miRNA-146a, miRNA-223, TLR4/TRAF6/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and HIF-1α.Biol Res. 2024 Jul 20;57(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00527-9. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 39033184 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of 6-Gingerol in Prevention of Colon Cancer Induced by Azoxymethane through the Modulation of Antioxidant Potential and Inflammation.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Dec 8;44(12):6218-6228. doi: 10.3390/cimb44120424. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36547085 Free PMC article.
-
6-gingerol ameliorates weight gain and insulin resistance in metabolic syndrome rats by regulating adipocytokines.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Mar;31(3):351-358. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.01.003. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 37026043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tominaga T., Abe H., Ueda O., Goto C., Nakahara K., Murakami T., Matsubara T., Mima A., Nagai K., Araoka T., et al. Activation of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4 Signaling Leads to Glomerulosclerosis That Mimics Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:20109–20116. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.179382. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ohkubo Y., Kishikawa H., Araki E., Miyata T., Isami S., Motoyoshi S., Kojima Y., Furuyoshi N., Shichiri M. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: A randomized prospective 6-year study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1995;28:103–117. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(95)01064-K. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

