Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clonal Complex 398 as a Major MRSA Lineage in Dogs and Cats in Thailand
- PMID: 33671008
- PMCID: PMC7997496
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10030243
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clonal Complex 398 as a Major MRSA Lineage in Dogs and Cats in Thailand
Abstract
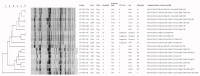
The aim of this study was to present molecular and antimicrobial resistance characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) clonal complex (CC) 398 isolated from diseased dogs and cats in Thailand. A total of 20 MRSA isolates of 134 Staphylococcus aureus isolated from canine and feline clinical samples during 2017-2020 were CC398, consisting of sequence type (ST) 398 (18 isolates), ST5926 (1 isolate), and ST6563 (1 isolate) by multilocus sequence typing. spa t034 and staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) V were predominantly associated with ST398. Intraclonal differentiation was present by additional spa (t1255, t4653), non-detectable spa, composite SCCmec with a hybrid of ccrA1B1+ccrC and class A mec complex, and DNA fingerprints by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. The isolates essentially carried antimicrobial resistance genes, mediating multiple resistance to β-lactams (mecA, blaZ), tetracyclines [tet(M)], aminoglycosides [aac(6')-Ie-aph(2')-Ia], and trimethoprim (dfr). Livestock-associated MRSA ST398 resistance genes including lnu(B), lsa(E), spw, fexA, and tet(L) were heterogeneously found and lost in subpopulation, with the absence or presence of additional erm(A), erm(B), and ileS2 genes that corresponded to resistance phenotypes. As only a single CC398 was detected with the presence of intraclonal variation, CC398 seems to be the successful MRSA clone colonizing in small animals as a pet-associated MRSA in Thailand.
Keywords: MRSA; antimicrobial resistance; cat; clonal complex 398; dog.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

