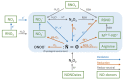
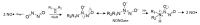Synthetic, Natural, and Semisynthetic Polymer Carriers for Controlled Nitric Oxide Release in Dermal Applications: A Review
- PMID: 33671032
- PMCID: PMC7957520
- DOI: 10.3390/polym13050760
Synthetic, Natural, and Semisynthetic Polymer Carriers for Controlled Nitric Oxide Release in Dermal Applications: A Review
Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO•) is a free radical gas, produced in the human body to regulate physiological processes, such as inflammatory and immune responses. It is required for skin health; therefore, a lack of NO• is known to cause or worsen skin conditions related to three biomedical applications- infection treatment, injury healing, and blood circulation. Therefore, research on its topical release has been increasing for the last two decades. The storage and delivery of nitric oxide in physiological conditions to compensate for its deficiency is achieved through pharmacological compounds called NO-donors. These are further incorporated into scaffolds to enhance therapeutic treatment. A wide range of polymeric scaffolds has been developed and tested for this purpose. Hence, this review aims to give a detailed overview of the natural, synthetic, and semisynthetic polymeric matrices that have been evaluated for antimicrobial, wound healing, and circulatory dermal applications. These matrices have already set a solid foundation in nitric oxide release and their future perspective is headed toward an enhanced controlled release by novel functionalized semisynthetic polymer carriers and co-delivery synergetic platforms. Finally, further clinical tests on patients with the targeted condition will hopefully enable the eventual commercialization of these systems.
Keywords: NO-donor; blood circulation; microbial infections; polymeric matrices; semisynthetic polymers; topical release; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Li B., Ming Y., Liu Y., Xing H., Fu R., Li Z., Ni R., Li L., Duan D., Xu J., et al. Recent Developments in Pharmacological Effect, Mechanism and Application Prospect of Diazeniumdiolates. [(accessed on 27 February 2021)];Front. Pharmacol. 2020 11:923. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00923. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fphar.2020.00923/full. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pelegrino M.T., de Araújo D.R., Seabra A.B. S-nitrosoglutathione-containing chitosan nanoparticles dispersed in Pluronic F-127 hydrogel: Potential uses in topical applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018;43:211–220. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2017.10.016. - DOI
-
- Opländer C., Römer A., Paunel-Görgülü A., Fritsch T., van Faassen E.E., Mürtz M., Bozkurt A., Grieb G., Fuchs P., Pallua N., et al. Dermal Application of Nitric Oxide In Vivo: Kinetics, Biological Responses, and Therapeutic Potential in Humans. [(accessed on 27 February 2021)];Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012 91:1074–1082. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2011.366. Available online: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1038/clpt.2011.366. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liechty W.B., Kryscio D.R., Slaughter B.V., Peppas N.A. Polymers for Drug Delivery Systems. [(accessed on 27 February 2021)];Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2010 1:149–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-073009-100847. Available online: https://pmc/articles/PMC3438887/?report=abstract. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources