Genetic Regulation of Tryptase Production and Clinical Impact: Hereditary Alpha Tryptasemia, Mastocytosis and Beyond
- PMID: 33671092
- PMCID: PMC7957558
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052458
Genetic Regulation of Tryptase Production and Clinical Impact: Hereditary Alpha Tryptasemia, Mastocytosis and Beyond
Abstract
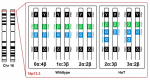
Tryptase is a serine protease that is predominantly produced by tissue mast cells (MCs) and stored in secretory granules together with other pre-formed mediators. MC activation, degranulation and mediator release contribute to various immunological processes, but also to several specific diseases, such as IgE-dependent allergies and clonal MC disorders. Biologically active tryptase tetramers primarily derive from the two genes TPSB2 (encoding β-tryptase) and TPSAB1 (encoding either α- or β-tryptase). Based on the most common gene copy numbers, three genotypes, 0α:4β, 1α:3β and 2α:2β, were defined as "canonical". About 4-6% of the general population carry germline TPSAB1-α copy number gains (2α:3β, 3α:2β or more α-extra-copies), resulting in elevated basal serum tryptase levels. This condition has recently been termed hereditary alpha tryptasemia (HαT). Although many carriers of HαT appear to be asymptomatic, a number of more or less specific symptoms have been associated with HαT. Recent studies have revealed a significantly higher HαT prevalence in patients with systemic mastocytosis (SM) and an association with concomitant severe Hymenoptera venom-induced anaphylaxis. Moreover, HαT seems to be more common in idiopathic anaphylaxis and MC activation syndromes (MCAS). Therefore, TPSAB1 genotyping should be included in the diagnostic algorithm in patients with symptomatic SM, severe anaphylaxis or MCAS.
Keywords: hereditary alpha tryptasemia; mastocytosis; tryptase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study. Outside of this study, G.G. and G.H. received honoraria from Novartis. P.V. served as a consultant in a global Novartis trial investigating the effects of midostaurin in patients with advanced systemic mastocytosis and received honoraria and research grants from Novartis, Blueprint, Pfizer, Ariad, Incyte, Celgene, and Deciphera. W.R.S. received honoraria from Novartis. G.U. received honoraria and grants from Ariad, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Incyte, Novartis, and Pfizer. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hereditary α tryptasemia is a valid genetic biomarker for severe mediator-related symptoms in mastocytosis.Blood. 2021 Jan 14;137(2):238-247. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020006157. Blood. 2021. PMID: 32777817 Free PMC article.
-
Heritable risk for severe anaphylaxis associated with increased α-tryptase-encoding germline copy number at TPSAB1.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021 Feb;147(2):622-632. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.06.035. Epub 2020 Jul 24. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32717252
-
The Genetic Basis and Clinical Impact of Hereditary Alpha-Tryptasemia.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 Jun;9(6):2235-2242. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2021.03.005. Epub 2021 Mar 17. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021. PMID: 33744473
-
Clinical relevance of inherited genetic differences in human tryptases: Hereditary alpha-tryptasemia and beyond.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021 Dec;127(6):638-647. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2021.08.009. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34400315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incorporating Tryptase Genotyping Into the Workup and Diagnosis of Mast Cell Diseases and Reactions.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022 Aug;10(8):1964-1973. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2022.05.003. Epub 2022 May 18. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022. PMID: 35597543 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Computational modeling of mast cell tryptase family informs selective inhibitor development.iScience. 2024 Aug 21;27(9):110739. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110739. eCollection 2024 Sep 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39280611 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Changes in Mastocytes and Their Significance in Mast Cell Tumor Prognosis and Treatment.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 22;15(1):137. doi: 10.3390/genes15010137. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hereditary α-Tryptasemia and Peripheral Blood KIT D816V Mutation in Patients with Pediatric Mastocytosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 23;26(13):6023. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136023. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649802 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Significance of Tryptase for Suspected Mast Cell Disorders.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Dec 14;13(24):3662. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13243662. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using the Right Criteria for MCAS.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024 Feb;24(2):39-51. doi: 10.1007/s11882-024-01126-0. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024. PMID: 38243020 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ehrlich P. Beiträge zur kenntniss der granulirten bindegewebszellen und der eosinophilen leukocythen. Arch. Anat. Physiol. 1879;3:166–169.
-
- Ehrlich P. Beiträge zur kenntniss der anilinfärbungen und ihrer verwendung in der mikroskopischen technik. Arch. Mikr. Anat. 1877;13:263–278. doi: 10.1007/BF02933937. - DOI
-
- Valent P., Akin C., Hartmann K., Nilsson G., Reiter A., Hermine O., Sotlar K., Sperr W.R., Escribano L., George T.I., et al. Mast cells as a unique hematopoietic lineage and cell system: From Paul Ehrlich’s visions to precision medicine concepts. Theranostics. 2020;10:10743–10768. doi: 10.7150/thno.46719. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical