Effects of the Novel PFKFB3 Inhibitor KAN0438757 on Colorectal Cancer Cells and Its Systemic Toxicity Evaluation In Vivo
- PMID: 33671096
- PMCID: PMC7957803
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13051011
Effects of the Novel PFKFB3 Inhibitor KAN0438757 on Colorectal Cancer Cells and Its Systemic Toxicity Evaluation In Vivo
Abstract
Background: Despite substantial progress made in the last decades in colorectal cancer (CRC) research, new treatment approaches are still needed to improve patients' long-term survival. To date, the promising strategy to target tumor angiogenesis metabolically together with a sensitization of CRC to chemo- and/or radiotherapy by PFKFB3 (6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase-3) inhibition has never been tested. Therefore, initial evaluation and validation of newly developed compounds such as KAN0438757 and their effects on CRC cells are crucial steps preceding to in vivo preclinical studies, which in turn may consolidate new therapeutic targets.
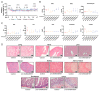
Materials and methods: The efficiency of KAN0438757 to block PFKFB3 expression and translation in human CRC cells was evaluated by immunoblotting and real-time PCR. Functional in vitro assays assessed the effects of KAN0438757 on cell viability, proliferation, survival, adhesion, migration and invasion. Additionally, we evaluated the effects of KAN0438757 on matched patient-derived normal and tumor organoids and its systemic toxicity in vivo in C57BL6/N mice.
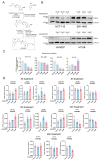
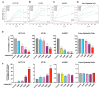
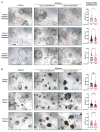
Results: High PFKFB3 expression is correlated with a worse survival in CRC patients. KAN0438757 reduces PFKFB3 protein expression without affecting its transcriptional regulation. Additionally, a concentration-dependent anti-proliferative effect was observed. The migration and invasion capacity of cancer cells were significantly reduced, independent of the anti-proliferative effect. When treating colonic patient-derived organoids with KAN0438757 an impressive effect on tumor organoids growth was apparent, surprisingly sparing normal colonic organoids. No high-grade toxicity was observed in vivo.
Conclusion: The PFKFB3 inhibitor KAN0438757 significantly reduced CRC cell migration, invasion and survival. Moreover, on patient-derived cancer organoids KAN0438757 showed significant effects on growth, without being overly toxic in normal colon organoids and healthy mice. Our findings strongly encourage further translational studies to evaluate KAN0438757 in CRC therapy.
Keywords: KAN0438757; PFKFB3; colon cancer; glycolysis; intestinal organoids; rectal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Paschke S., Jafarov S., Staib L., Kreuser E.D., Maulbecker-Armstrong C., Roitman M., Holm T., Harris C.C., Link K.H., Kornmann M. Are Colon and Rectal Cancer Two Different Tumor Entities? A Proposal to Abandon the Term Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018;19:2577. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092577. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cantelmo A.R., Conradi L.C., Brajic A., Goveia J., Kalucka J., Pircher A., Chaturvedi P., Hol J., Thienpont B., Teuwen L.A., et al. Inhibition of the Glycolytic Activator PFKFB3 in Endothelium Induces Tumor Vessel Normalization, Impairs Metastasis, and Improves Chemotherapy. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:968–985. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

