Nutraceuticals in the Prevention of Viral Infections, including COVID-19, among the Pediatric Population: A Review of the Literature
- PMID: 33671104
- PMCID: PMC7957644
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052465
Nutraceuticals in the Prevention of Viral Infections, including COVID-19, among the Pediatric Population: A Review of the Literature
Abstract
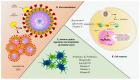
In recent years, there has been a growth in scientific interest in nutraceuticals, which are those nutrients in foods that have beneficial effects on health. Nutraceuticals can be extracted, used for food supplements, or added to foods. There has long been interest in the antiviral properties of nutraceuticals, which are especially topical in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, the purpose of this review is to evaluate the main nutraceuticals to which antiviral roles have been attributed (either by direct action on viruses or by modulating the immune system), with a focus on the pediatric population. Furthermore, the possible applications of these substances against SARS-CoV-2 will be considered.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV2; children; hesperidin; lactoferrin; nutraceutical; probiotics; quercetin; resveratrol; viral infections; vitamin; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adjunctive Nutraceutical Therapies for COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 16;22(4):1963. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041963. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: A review.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020 Jul-Aug;14(4):367-382. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020. PMID: 32334392 Free PMC article.
-
Nutraceuticals in Viral Infections: An Overview of the Immunomodulating Properties.Nutrients. 2021 Jul 14;13(7):2410. doi: 10.3390/nu13072410. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34371920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can nutraceuticals assist treatment and improve covid-19 symptoms?Nat Prod Res. 2022 May;36(10):2672-2691. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2021.1914032. Epub 2021 May 5. Nat Prod Res. 2022. PMID: 33949266 Review.
-
Dietary Supplements and Nutraceuticals under Investigation for COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment.mSystems. 2021 May 4;6(3):e00122-21. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00122-21. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 33947804 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
UPLC-ESI-QTRAP-MS/MS Analysis to Quantify Bioactive Compounds in Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.) Waste with Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity.Metabolites. 2022 Jul 27;12(8):701. doi: 10.3390/metabo12080701. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36005573 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphenol-Rich Larix decidua Bark Extract with Antimicrobial Activity against Respiratory-Tract Pathogens: A Novel Bioactive Ingredient with Potential Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Applications.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jun 28;10(7):789. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070789. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34203520 Free PMC article.
-
Ayurvedic formulations: Potential COVID-19 therapeutics?Phytomed Plus. 2022 Aug;2(3):100286. doi: 10.1016/j.phyplu.2022.100286. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Phytomed Plus. 2022. PMID: 35474908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like Receptor Mediation in SARS-CoV-2: A Therapeutic Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 14;23(18):10716. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810716. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Iron Chelation and Protease Inhibition of Natural Products on COVID-19 Infection.J Clin Med. 2021 May 25;10(11):2306. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112306. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34070628 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus-19. [(accessed on 25 October 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

