Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of Mitotic-Specific 3,4-Dihydropyridine-2(1 H)-thiones
- PMID: 33671106
- PMCID: PMC7957618
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22052462
Synthesis and Anticancer Activity of Mitotic-Specific 3,4-Dihydropyridine-2(1 H)-thiones
Abstract
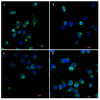
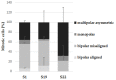
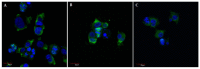
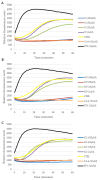
Most anticancer drugs target mitosis as the most crucial and fragile period of rapidly dividing cancer cells. However the limitations of classical chemotherapeutics drive the search for new more effective and selective compounds. For this purpose structural modifications of the previously characterized pyridine aalog (S1) were incorporated aiming to obtain an antimitotic inhibitor of satisfactory and specific anticancer activity. Structure-activity relationship analysis of the compounds against a panel of cancer cell lines allowed to select a compound with a thiophene ring at C5 of a 3,4-dihydropyridine-2(1H)-thione (S22) with promising antiproliferative activity (IC50 equal 1.71 ± 0.58 µM) and selectivity (SI = 21.09) against melanoma A375 cells. Moreover, all three of the most active compounds from the antiproliferative study, namely S1, S19 and S22 showed better selectivity against A375 cells than reference drug, suggesting their possible lower toxicity and wider therapeutic index. As further study revealed, selected compounds inhibited tubulin polymerization via colchicine binding site in dose dependent manner, leading to aberrant mitotic spindle formation, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Summarizing, the current study showed that among obtained mitotic-specific inhibitors analogue with thiophene ring showed the highest antiproliferative activity and selectivity against cancer cells.
Keywords: anticancer agents; colchicine-binding site; dihydropyridine; mitotic spindle; tubulin inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Design and discovery of new antiproliferative 1,2,4-triazin-3(2H)-ones as tubulin polymerization inhibitors targeting colchicine binding site.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Jul;112:104965. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104965. Epub 2021 May 5. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34020238
-
New thiazole-2(3H)-thiones containing 4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl) moiety as anticancer agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Jan 1;185:111784. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111784. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31669850
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel benzo[c]acridine-diones as potential anticancer agents and tubulin polymerization inhibitors.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2019 Jun;352(6):e1800307. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201800307. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2019. PMID: 31012156
-
The Expanding Role of Pyridine and Dihydropyridine Scaffolds in Drug Design.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Oct 13;15:4289-4338. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S329547. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34675489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical appraisals of approaches for predictive designs in anticancer drugs.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002 Jun;59(6):959-1023. doi: 10.1007/s00018-002-8483-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 12169026 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the antitumor potential of novel quinoline derivatives via tubulin polymerization inhibition in breast cancer; design, synthesis and molecular docking.RSC Adv. 2024 Jul 12;14(31):22092-22112. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04371e. eCollection 2024 Jul 12. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39005243 Free PMC article.
-
The Co-Administration of Paclitaxel with Novel Pyridine and Benzofuran Derivatives that Inhibit Tubulin Polymerisation: A Promising Anticancer Strategy.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 9;17(2):223. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020223. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006590 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

